https://terragrunt.gruntwork.io/
Thin CLI wrapper around Terraform which adds lots of sourcing and templating capabilities.
- Key Points
- Install
- Terragrunt Template
- Terragrunt Usage
- Terraform Lock Files
- Terragrunt Console
- Dependencies
- Terragrunt Scaffold
- Linting and Security Scanning
- tgswitch
- Best Practices
- Vendor Code
- Terragrunt Debugging
- Terragrunt Troubleshooting
Uses same arguments which are passed to the terraform command.
Designed to reduce duplication when using Terraform code by adding support for variables, expressions, functions and
relative roots in provider and backend blocks.
Enables running Terraform modules individually to save run time.
Essentially turns shared modules (eg. from a registry) into root modules like you'd normally terraform init to
deploy the infrastructure.
In CI/CD pipelines you often only want to deploy the modules which have changed individually instead of the entire terraform code base, because Terraform is slow (usually because it has to make lots of calls to cloud APIs to determine what changes need to be made).
In that case each module then needs its own backend configuration which is almost the same apart from key file path and is otherwise all duplication, which Terragrunt can source to deduplicate.
Advocates DRY configuration every 10 seconds, which ironically stands for Don't Repeat Yourself.
Someone needs to create a doc tool to DRY out all the Terragrunt documentation references to DRY ;)
Quicker if you've got DevOps-Bash-tools - finds and installs the latest version:
install_terragrunt.shInstall shell autocomplete:
terragrunt --install-autocompleteHeavily commented with advanced knowledge.
Edit to suit your needs:
HariSekhon/Terraform - terragrunt.hcl
Then run...
Passes all args straight to the terraform command except for --version and --terragrunt-*.
Almost the same commands as regular terraform, just replace terraform with terragrunt:
Auto-init means you don't need to run terragrunt init,
it is automatically called during terragrunt plan if it detects it's not been initialized.
terragrunt planterragrunt applyhttps://terragrunt.gruntwork.io/docs/reference/cli-options/#validate-inputs
Finds:
- required inputs for a module that are missing
- unused inputs being passed to a terraform module for which it is not expecting.
Strict mode exits with error instead of just printing a warning:
terragrunt validate-inputs --terragrunt-strict-validateUse this in CI/CD to force people to properly maintain their code changes.
Recursively looks for terragrunt.hcl in all subdirectories and concurrently runs them (run these from the root
directory of your terragrunt'd terraform repo).
WARNING: adds implicit -auto-approve and doesn't prompt (don't use it with destroy argument!)
terragrunt run-all validateterragrunt run-all plan # --terragrunt-out-dir /tmp/tfplanterragrunt run-all apply # --terragrunt-out-dir /tmp/tfplanSee also the Graph Run command further down.
You can add --terragrunt-no-auto-approve / TERRAGRUNT_NO_AUTO_APPROVE=true to prevent this, but due to
interactive prompts will implicitly also add --terragrunt-parallelism 1.
Recursively finds .hcl files and formats them:
terragrunt hclfmt--terragrunt-parallelism 4- avoid hitting rate limiting with Cloud providers APIs--terragrunt-out-dir /tmp/tfplan- save the plan and apply it exactly. Forrun-allthetfplan.tfplanfiles are saved in subdirectories of the same naming structure--terragrunt-json-out-dir- save the plan in JSON format. Can be used together with the above switch to save both formats, one for text investigation and the other for applying
For CI/CD, set environment variable:
TERRAGRUNT_NON_INTERACTIVE=trueThe .terraform.lock.hcl is generated in the same directory as your terragrunt.hcl file.
When Terragrunt downloads remote configurations into a sub-directory like .terragrunt-cache/<url>/<remote_code>
it copies the top level .terraform.lock.hcl file into the sub-directory before running Terraform and back to $PWD
after the run to capture the changes.
Commit your lock file as per Terraform standard to ensure your colleagues get the same provider versions.
Useful for testing.
terragrunt consoleTerragrunt functions like get_parent_terragrunt_dir() don't work in the REPL unfortunately.
Rest is same as Terraform Console.
Since Terragrunt splits things into lots of modules, you often want to cross reference each other dynamically like this:
dependency "s3" {
config_path = "${find_in_parent_folders("s3")}/my-config"
}
...
s3_bucket_name = dependency.s3.outputs.s3_bucket_id
s3_bucket_arn = dependency.s3.outputs.s3_bucket_arnDon't forget the .outputs. part of the dependency reference to get its output variables.
To check the outputs of the dependency module:
cd s3/some-bucket-moduleterragrunt outputsoutput will look something like this:
s3_bucket_arn = "arn:aws:s3:::my-config"
s3_bucket_bucket_domain_name = "my-config.s3.amazonaws.com"
s3_bucket_bucket_regional_domain_name = "my-config.s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com"
s3_bucket_hosted_zone_id = "A1BCDEFA23BCDE"
s3_bucket_id = "my-config"
s3_bucket_region = "eu-west-1"
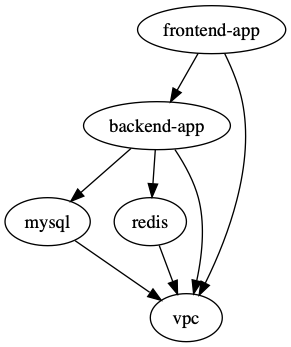
Recurse sub-directories and generate a dependency graph based on the dependency and dependencies blocks:
terragrunt graph-dependencies | dot -Tsvg > graph.svgOn Mac you can open the graph from the command line too:
open graph.svgThis is the order of "depends on" - Terragrunt will run the modules from the bottom up.
You can execute a command against all module dependencies of the current module directory.
Beware although not documented, this like assumes -auto-approve so make sure to plan and check first:
terragrunt graph planterragrunt graph applyTerragrunt contains built-in templating.
This command will find the latest release tag of the given module and generate the
boilerplate terragrunt.hcl for you including the tagged source url
and the input variables for the given module (WARNING: the scaffold command overwrites any terragrunt.hcl file
in the local directory without prompting):
terragrunt scaffold github.com/gruntwork-io/terragrunt-infrastructure-modules-example//modules/mysqlCan set ref version and SSH git source via variables, see this doc page.
You can then run checkov on the resulting json file:
checkov -f terragrunt_rendered.json --skip-check $(cat /home/atlantis/.checkov-skip.conf|tr '\\n' ',') --compact --quietEasily switch between Terragrunt versions.
See tgswitch
More recently updated than tgenv.
https://www.terraform-best-practices.com/
https://terragrunt.gruntwork.io/docs/features/provider-cache-server/
Because Terraform Plugin Caching is not thread-safe.
To use it, just:
export TG_PROVIDER_CACHE=1Stores plugins in:
$HOME/.cache/terragrunt/providers
or on Mac:
$HOME/Library/Caches/terragrunt/providers
You can set TG_PROVIDER_CACHE_DIR to override it (eg. on Atlantis to the larger
/atlantis-data partition):
export TG_PROVIDER_CACHE_DIR="/atlantis-data/plugin-cache"Don't forget to create that dir:
mkdir -p -v /atlantis-data/plugin-cache
chown atlantis:atlantis /atlantis-data/plugin-cacheTo cache from registries other than registry.terraform.io and registry.opentofu.org
eg. if you have your own private registry:
export TG_PROVIDER_CACHE_REGISTRY_NAMES="example1.com,example2.com"To see how much space you are wasting on duplicate provider downloads for Terragrunt modules, you can run this script from DevOps-Bash-tools:
terraform_provider_count_sizes.shOutput on my Mac:
30 597M hashicorp/aws/5.80.0/darwin_arm64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.80.0_x5
7 637M hashicorp/aws/5.90.1/darwin_arm64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.90.1_x5
4 637M hashicorp/aws/5.90.0/darwin_arm64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.90.0_x5
3 599M hashicorp/aws/5.81.0/darwin_arm64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.81.0_x5
2 593M hashicorp/aws/5.79.0/darwin_arm64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.79.0_x5
...
Output on an Atlantis server pod after deleting all data cache to fix out of space errors and then a single PR run:
14 654M hashicorp/aws/5.90.1/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.90.1_x5
13 14M hashicorp/external/2.3.4/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-external_v2.3.4_x5
13 14M hashicorp/local/2.5.2/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-local_v2.5.2_x5
13 14M hashicorp/null/3.2.3/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-null_v3.2.3_x5
3 346M hashicorp/aws/4.67.0/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-aws_v4.67.0_x5
3 621M hashicorp/aws/5.80.0/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.80.0_x5
3 653M hashicorp/aws/5.90.0/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.90.0_x5
3 14M hashicorp/random/3.6.3/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-random_v3.6.3_x5
1 627M hashicorp/aws/5.82.2/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.82.2_x5
1 630M hashicorp/aws/5.84.0/linux_amd64/terraform-provider-aws_v5.84.0_x5
Example code to portably follow the AWS Account ID and region of the codebase section:
locals {
environment_vars = read_terragrunt_config(find_in_parent_folders("account.hcl"))
aws_account_id = local.environment_vars.locals.aws_account_id
region_vars = read_terragrunt_config(find_in_parent_folders("region.hcl"))
aws_region = local.region_vars.locals.aws_region
}and used further down like this:
"arn:aws:iam::${local.aws_account_id}:...""${local.aws_region}.elasticache-snapshot.amazonaws.com"Instead of this:
dependency "s3" {
config_path = "../../s3/mybucket"
}Do this to maintain directory path depth structure portability:
dependency "s3" {
config_path = "${find_in_parent_folder("s3")}/mybucket"
}For example if you have a module that is 3 ../../../ levels deep
due to putting some external vendor specific modules under a subdirectory, the code will still work either way.
Read Terraform - Vendor Code section.
Use --terragrunt-log-level=debug.
Use --terragrunt-debug or export TERRAGRUNT_DEBUG=1 to create a $PWD/terragrunt-debug.tfvars.json file to be able to run terraform with the
same inputs without terragrunt.
terragrunt apply --terragrunt-log-level=debug --terragrunt-debugIn newer versions of Terragrunt use --inputs-debug instead of --terragrunt-debug
(it still creates terragrunt-debug.tfvars.json):
terragrunt apply --inputs-debugterragrunt-debug.tfvars.json allows you to inspect the variables that Terragrunt is generating and passing to the Terraform code.
See this doc page for more details and OpenTelemetry integration.
terragrunt plan -out=plan.tfplanterraform show -json plan.tfplan > plan.jsonOR
terragrunt run-all render-jsonFind the JSON output in:
terragrunt_rendered.json
To recover space or just clear cache
find . -name '.terragrunt-cache' -exec rm -rf {} \;If you get an error like this when running Terragrunt:
ERRO[0000] fork/exec /Users/hari/.tfenv/bin: no such file or directory
ERRO[0000] Unable to determine underlying exit code, so Terragrunt will exit with error code 1
then make sure to unset TERRAGRUNT_TFPATH or direct it to your correct terraform binary (rather than directory as
in the case above).
Error: Get "http://localhost/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/configmaps/aws-auth": dial tcp [::1]:80: connect: connection refused
╷
│ Error: Get "http://localhost/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/configmaps/aws-auth": dial tcp [::1]:80: connect: connection refused
│
│ with kubernetes_config_map.aws_auth[0],
│ on aws_auth.tf line 63, in resource "kubernetes_config_map" "aws_auth":
│ 63: resource "kubernetes_config_map" "aws_auth" {
│
╵
Workaround:
terragrunt state rm 'kubernetes_config_map.aws_auth[0]'Then run:
terragrunt applyIt'll apply the rest and fail on the aws_auth map, but you can re-import it:
terragrunt import 'kubernetes_config_map.aws_auth[0]' kube-system/aws-authIf you get an error like this when running Terraform or Terragrunt:
Error: Required plugins are not installed
The installed provider plugins are not consistent with the packages selected
in the dependency lock file:
- registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws: the cached package for registry.terraform.io/hashicorp/aws 5.80.0 (in .terraform/providers) does not match any of the checksums recorded in the dependency lock file
This is caused
by the .terraform.lock.hcl being generated and committed from a machine of a different architecture since
default Terraform only includes the checksums for the local architecture.
This surfaces in Atlantis or other CI/CD systems because developers are often using Mac (or heavy forbid Windows) but the CI/CD systems like Atlantis are invariably running on Linux.
Run this command to update the .terraform.lock.hcl file with the checksum for all 3 architectures:
terragrunt providers lock -platform=windows_amd64 -platform=darwin_amd64 -platform=linux_amd64and then commit the updated .terraform.lock.hcl file:
git add .terraform.lock.hcl
git commit -m "updated .terraform.lock.hcl file with checksums for all 3 platform architectures" .terraform.lock.hcl