Last active
September 29, 2023 01:37
-
-
Save GregTJ/6f3b86e7ef6a2e776174026ceae369ad to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
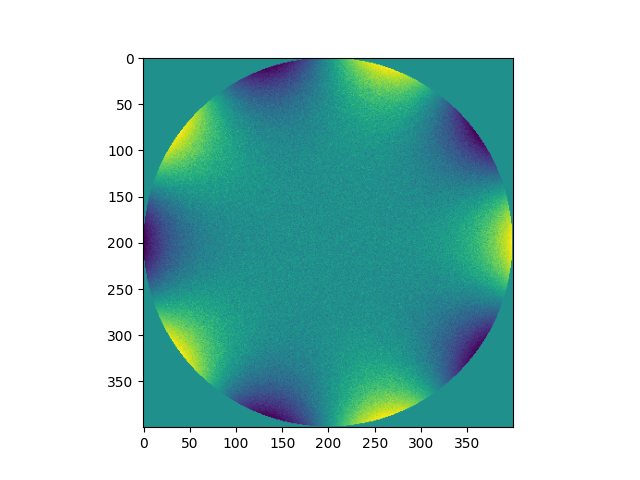
Naïve Walk On Spheres implementation for the Laplace equation on a disk with sinusoidal boundary values.
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| import numpy as np | |
| from matplotlib import pyplot as plt | |
| samples = 64 | |
| epsilon = 1e-3 | |
| domain = 400, 400 | |
| def boundary_value(a, freq=5): | |
| return np.sin(np.arctan2(*a) * freq) | |
| def closest_boundary(a): | |
| return np.divide(a, d := np.linalg.norm(a, axis=0), where=d != 0) | |
| grid = np.stack(np.meshgrid(*(np.linspace(-1, 1, d) for d in domain))) | |
| mask = np.linalg.norm(grid, axis=0) <= 1 | |
| rng = np.random.default_rng() | |
| result = np.zeros(domain) | |
| for s in range(samples): | |
| points = grid.copy() | |
| alive = mask.copy() | |
| radii = np.zeros(domain) | |
| angles = np.zeros(domain) | |
| closest = np.zeros_like(grid) | |
| while np.sum(alive) > 0: | |
| closest[:, alive] = closest_boundary(points[:, alive]) | |
| radii[alive] = np.linalg.norm(points[:, alive] - closest[:, alive], axis=0) | |
| alive[alive] = radii[alive] > epsilon | |
| angles[alive] = rng.uniform(-np.pi, np.pi, np.count_nonzero(alive)) | |
| points[:, alive] += np.stack((radii[alive] * np.cos(angles[alive]), | |
| radii[alive] * np.sin(angles[alive]))) | |
| result[mask] += boundary_value(closest)[mask] | |
| result /= samples | |
| plt.imshow(result) | |
| plt.show() |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
Result: