Source: https://medium.com/@Mahmoud_Zalt/eloquent-relationships-cheat-sheet-5155498c209
| One to one ( 1-1) |
One to many ( 1-n) |
Poly one to many ( 1x-n) |
Many to many ( n-n) |
Poly many to many ( nx-n) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of models | 2 only | 2 only | 3 and above | 2 only | 3 and above |
| Number of tables | 2 (1/model) | 2 (1/model) | 3+ (1/model) | 3 (1/model + pivot) | 4+ (1/model + pivot) |
| Pivot table | - | - | - | required | required |
| Model A relation | hasOne |
hasMany |
morhpMany (all) |
belongsToMany |
morphToMany (all) |
| Model B relation | belongsTo |
belongsTo |
morphTo |
belongsToMany |
morphToMany |
| Set relation on Model A | save(B) |
saveMany([B1, B2])save(B) |
saveMany([B1, B2])save(B) |
attach([B1, B2])sync([B1, B2]) |
saveMany([B1, B2])save(B) |
| Set relation on Model B | associate(A)->save() |
associate(A)->save() |
associate(A)->save() |
attach([A1, A2])sync([A1, A2]) |
attach([A1, A2])sync([A1, A2]) |
| Foreign key holder | Model B table (A_id) |
Model B table (A_id) |
Model B table (A_id, A_type) |
Pivot table (A_id, B_id) |
Pivot table (A_id, A_type, B_id) |
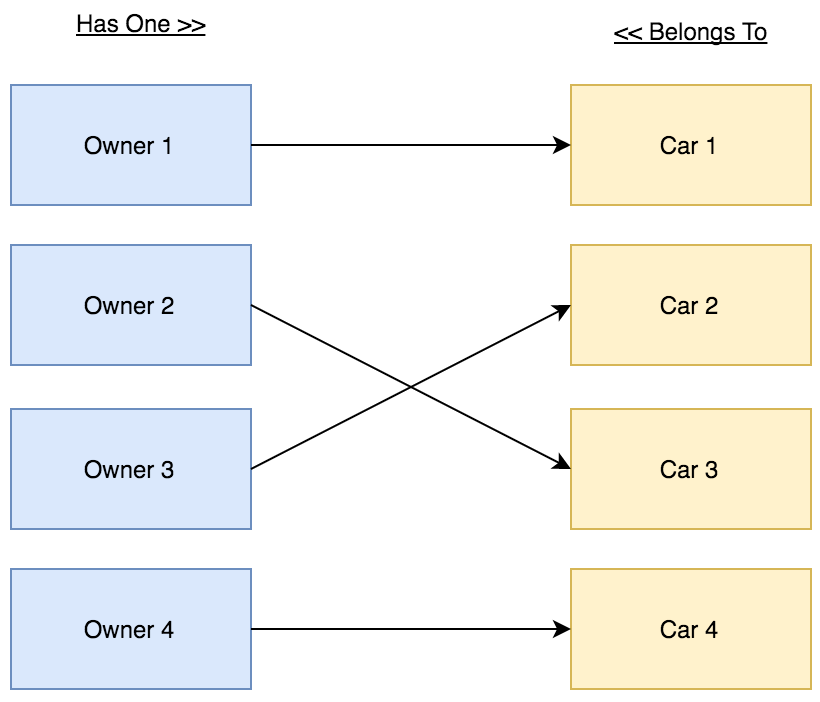
In this demo we have 2 models (Owner and Car), and 2 tables (owners and cars).
The Owner can own one Car. The Car can be owned by one Owner.
The Cars table should store the Owner ID.
class Owner
{
public function car()
{
return $this->hasOne(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function owner()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Owner::class);
}
}Schema::create('owners', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('owner_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->foreign('owner_id')->references('id')->on('owners');
});// Create relation between Owner and Car.
$owner->car()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and Owner.
$car->owner()->associate($owner)->save();// Get Owner Car
$owner->car;
// Get Car Owner
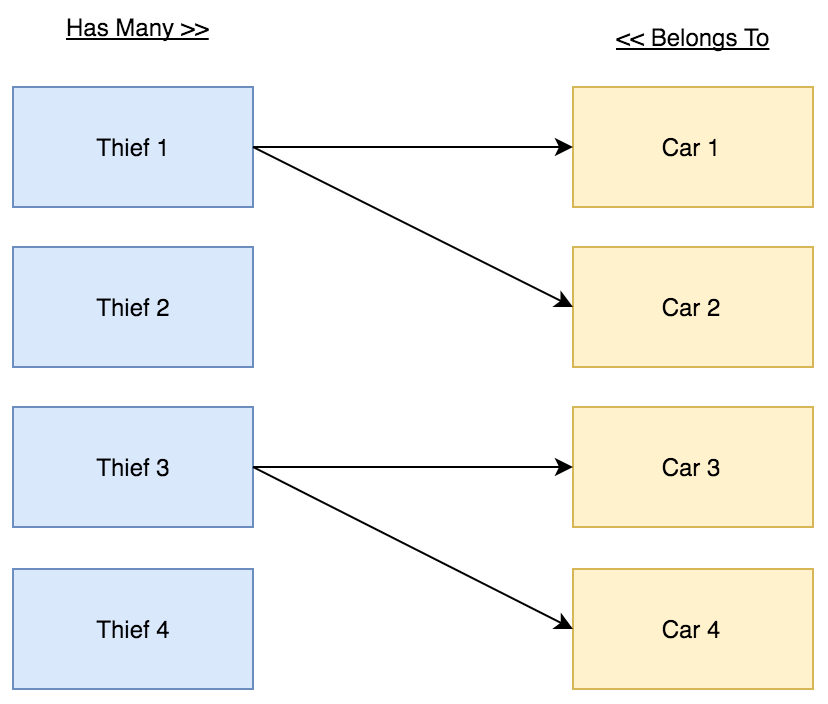
$car->owner;In this demo we have 2 models (Thief and Car), and 2 tables (thieves and cars).
The Thief can steal many Cars. The Car can be stolen by one Thief.
The Cars table should store the Thief ID.
class Thief
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->hasMany(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function thief()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Thief::class);
}
}Schema::create('thieves', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('thief_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->foreign('thief_id')->references('id')->on('thieves');
});// Create relation between Thief and Car.
$thief->cars()->saveMany([
$car1,
$car2,
]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$thief->cars()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and Thief.
$car->thief()->associate($thief)->save();// Get Thief Car
$thief->cars;
// Get Car Thief
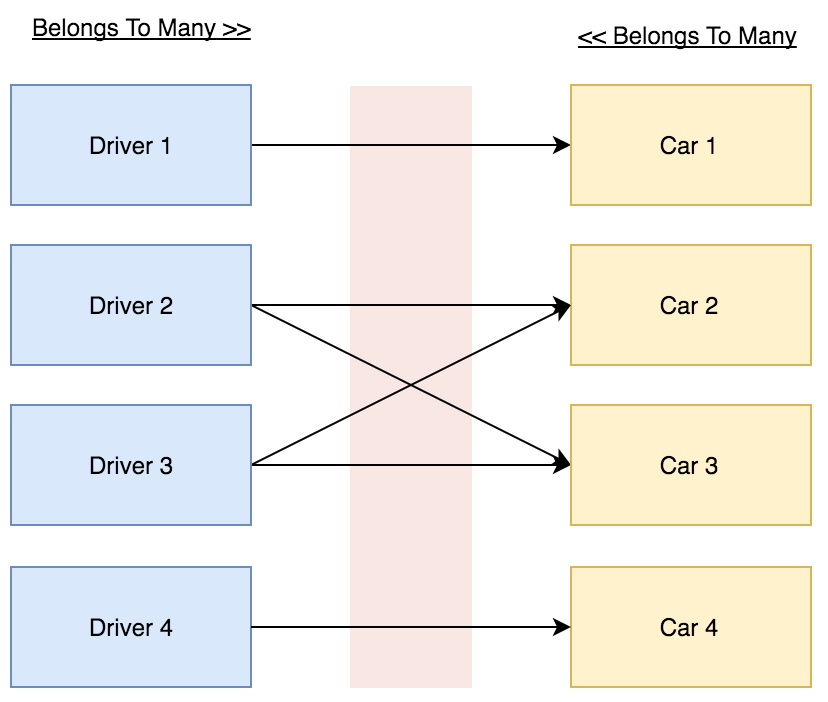
$car->thief;In this demo we have 2 models (Driver and Car), and 3 tables (drivers, cars and a pivot table named car_driver).
The Driver can drive many Cars. The Car can be driven by many Drivers.
The Pivot table “car_driver” should store the Driver ID and the Car ID.
class Driver
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function drivers()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Driver::class);
}
}Schema::create('drivers', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('car_driver', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->integer('car_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('car_id')->references('id')->on('cars')->onDelete('cascade');
$table->integer('driver_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('driver_id')->references('id')->on('drivers')->onDelete('cascade');
});// Create relation between Driver and Car.
$driver->cars()->attach([
$car1->id,
$car2->id,
]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$driver->cars()->sync([
$car1->id,
$car2->id,
]);
// Create relation between Car and Driver.
$car->drivers()->attach([
$driver1->id,
$driver2->id,
]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$car->drivers()->sync([
$driver1->id,
$driver2->id,
]);// Get Driver Car
$driver->cars
// Get Car Drivers
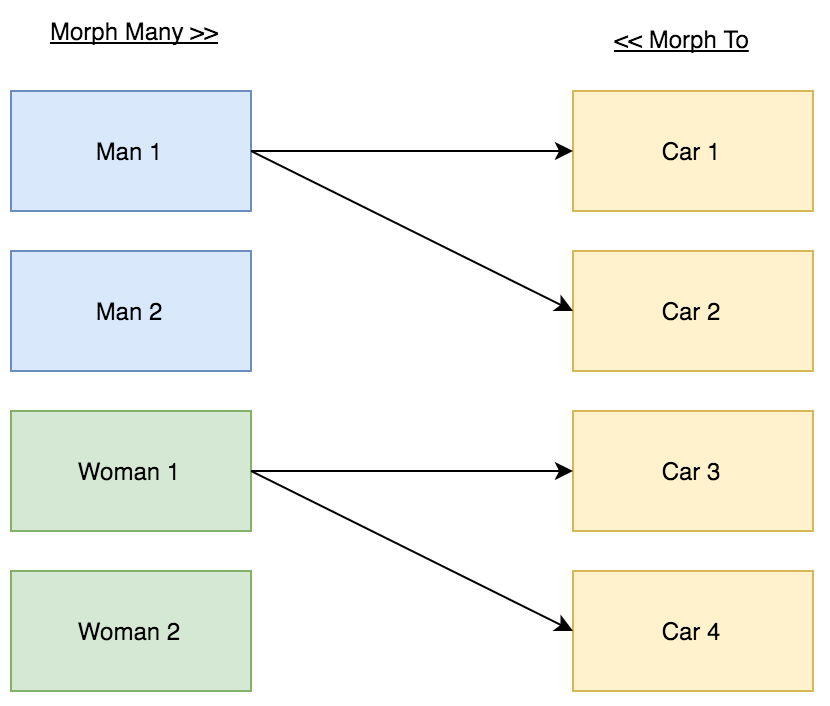
$car->driversIn this demo we have 3 models (Man, Woman and Car), and 3 tables (men, women and cars).
The Man (buyer) can buy many Cars. The Woman (buyer) can buy many Cars. The Car can be bought by one buyer (Man or Woman).
The Car table should store the Buyer ID and the Buyer Type. “buyer” is a name given to a group of models (Man and Woman). And it’s not limited to two. The buyer type is the real name of the model.
class Man
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphMany(Car::class, 'buyer');
}
}
class Woman
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphMany(Car::class, 'buyer');
}
}
class Car
{
public function buyer()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}
}Schema::create('men', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('women', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('buyer_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->string('buyer_type')->nullable();
});// Create relation between buyer (Man/Woman) and Car.
$man->cars()->saveMany([
$car1,
$car2,
]);
$woman->cars()->saveMany([
$car1,
$car2,
]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$man->cars()->save($car);
$woman->cars()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and buyer (Men/Women).
$car1->buyer()->associate($man)->save();
$car2->buyer()->associate($woman)->save();// Get buyer (Man/Woman) Cars
$men->cars
$women->cars
// Get Car buyer (Man and Woman)
$car->buyerIn this demo we have 3 models (Valet, Owner and Car), and 4 tables (valets, owners, cars and drivers).
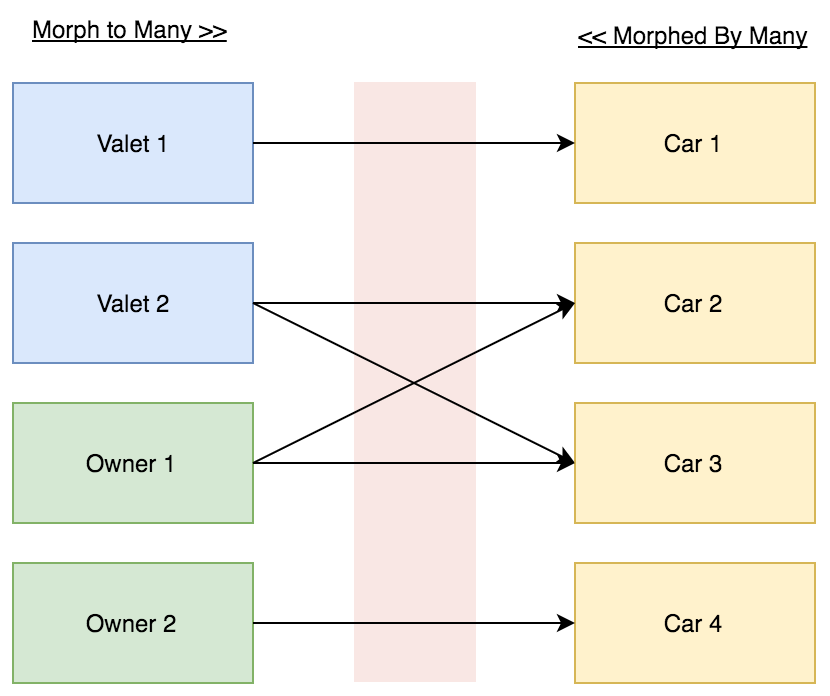
The Valet (driver) can drive many Cars. The Owner (driver) can drive many Cars. The Car can be driven by many drivers (Valet or/and Owner).
The Pivot table “drivers” should store the Driver ID, Driver Type and the Car ID. “driver” is a name given to a group of models (Valet and Owner). And it’s not limited to two. The driver type is the real name of the model.
class Valet
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphToMany(Car::class, 'driver');
}
}
class Owner
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphToMany(Car::class, 'driver');
}
}
class Car
{
public function valets()
{
return $this->morphedByMany(Man::class, 'driver');
}
public function owners()
{
return $this->morphedByMany(Woman::class, 'driver');
}
}Schema::create('valets', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('owners', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('drivers', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->integer('driver_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->string('driver_type');
$table->integer('car_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('car_id')->references('id')->on('cars')->onDelete('cascade');
});// Create relation between driver (Valet/Owner) and Car.
$valet->cars()->saveMany([$car1, $car2]);
$owner->cars()->saveMany([$car1, $car2]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$valet->cars()->save($car1);
$owner->cars()->save($car1);
// Create relation between Car and driver (Valet/Owner).
$car->valets()->attach([
$valet1->id,
$valet2->id,
]);
$car->owners()->attach([
$owner1->id,
$owner2->id,
]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$car->valets()->sync([
$valet1->id,
$valet2->id,
]);
$car->owners()->sync([
$owner1->id,
$owner2->id,
]);// Get driver (Valet/Owner) Cars
$valet->cars
$owner->cars
// Get Car drivers (Valet and Owner)
$car->owners
$car->valets