Created
May 15, 2018 16:11
-
-
Save bzamecnik/0bbe1e35ed7cc41bcaa4da9856f0ad38 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
Working example of StagingArea GPU prefetch using Tensorpack + Keras.
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| #!/usr/bin/env python | |
| # Author: Bohumir Zamecnik, Yuxin Wu (original example mnist-keras.py) | |
| import tensorflow as tf | |
| from tensorflow import keras | |
| KL = keras.layers | |
| """ | |
| An example asynchronous host-to-device memcpy using a Keras model + Tensorpack. | |
| It's a convnet with larger batches of random CIFAR10-sized data (1.5 M / batch) | |
| and is trained using pure Tensorpack trainer. The data is created in parallel | |
| using a PrefetchDataZMQ, then fed to TF-memory using TF Qeueu (QueueInput) and | |
| to StagingArea at GPU using StagingInput. | |
| It really works. | |
| Note that StagingArea for the same model does not work now when using KerasModel wrapper. | |
| - tensorpack 0.8.5 (eb2492c4f7b5e9b52de2af945ab190e824a6d7ee) | |
| - Keras 2.1.6 | |
| - tensorflow-gpu=1.8.0 | |
| Nvidia GTX 1080 Ti | |
| """ | |
| from tensorpack import * | |
| from tensorpack.utils.argtools import memoized | |
| from tensorpack.contrib.keras import KerasPhaseCallback | |
| IMAGE_SIZE = 32 | |
| @memoized # this is necessary for sonnet/Keras to work under tensorpack | |
| def get_keras_model(): | |
| # same architecture as in https://gist.github.com/bzamecnik/b9dbd50cdc195d54513cd2f9dfb7e21b | |
| M = keras.models.Sequential() | |
| M.add(KL.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu', input_shape=[IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3], padding='same')) | |
| M.add(KL.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')) | |
| M.add(KL.MaxPooling2D()) | |
| M.add(KL.Dropout(0.25)) | |
| M.add(KL.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')) | |
| M.add(KL.Conv2D(64, 3, activation='relu', padding='same')) | |
| M.add(KL.MaxPooling2D()) | |
| M.add(KL.Dropout(0.25)) | |
| M.add(KL.Flatten()) | |
| M.add(KL.Dense(512, activation='relu')) | |
| M.add(KL.Dropout(0.5)) | |
| M.add(KL.Dense(10, activation=None)) | |
| return M | |
| class Model(ModelDesc): | |
| def inputs(self): | |
| return [tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3), 'input'), | |
| tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None, 1), 'label')] | |
| def build_graph(self, image, label): | |
| # image = tf.expand_dims(image, 3) * 2 - 1 | |
| label = label[:, 0] | |
| M = get_keras_model() | |
| logits = M(image) | |
| # build cost function by tensorflow | |
| cost = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=label) | |
| cost = tf.reduce_mean(cost, name='cross_entropy_loss') # the average cross-entropy loss | |
| return cost | |
| def optimizer(self): | |
| lr = tf.train.exponential_decay( | |
| learning_rate=1e-3, | |
| global_step=get_global_step_var(), | |
| decay_steps=468 * 10, | |
| decay_rate=0.3, staircase=True, name='learning_rate') | |
| tf.summary.scalar('lr', lr) | |
| return tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr) | |
| if __name__ == '__main__': | |
| # logger.auto_set_dir() | |
| dataset_train = BatchData(FakeData( | |
| shapes=[(32, 32, 3), (1,)], | |
| dtype=['float32', 'uint8'], | |
| domain=[(0, 1), (0, 10)], | |
| size=51200), 128) | |
| dataset_train = PrefetchDataZMQ(PrintData(dataset_train), 2, 2) | |
| input_train = QueueInput(dataset_train) | |
| input_train = StagingInput(input_train) | |
| cfg = TrainConfig( | |
| model=Model(), | |
| data=input_train, | |
| # dataflow=dataset_train, | |
| callbacks=[ | |
| KerasPhaseCallback(True), # for Keras training | |
| # ModelSaver(), | |
| # InferenceRunner( | |
| # dataset_test, | |
| # ScalarStats(['cross_entropy_loss', 'accuracy'])), | |
| ], | |
| max_epoch=2, | |
| ) | |
| launch_train_with_config(cfg, SimpleTrainer()) |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
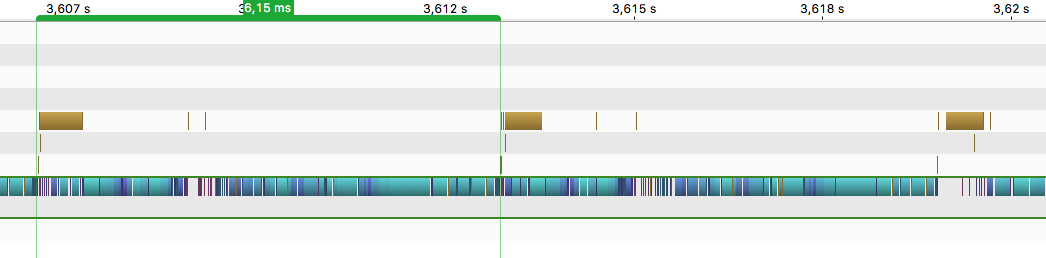
Without staging (memcpy is synchronous - kernels wait for it):
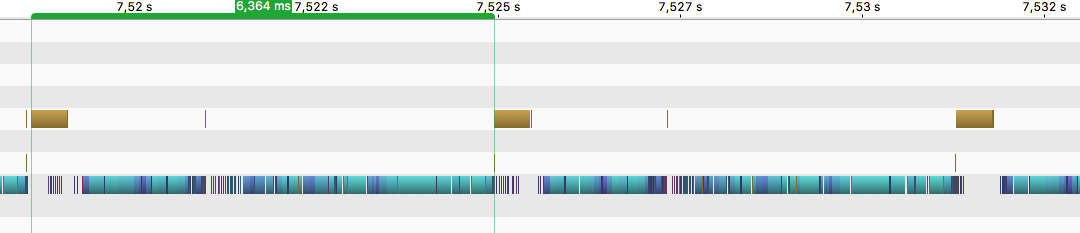
With staging (kernels do not wait, since they have data already at hand):