Using HPE Remote Copy Peer Persistence with Red Hat OpenShift and the HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes
For nearly two decades, Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Red Hat have had a long standing partnership providing jointly supported software, platforms and services including many reference architectures and configurations which support HPE and Red Hat customers in their container initiatives. Whether you’re building physical, virtual, or cloud environments, you can be confident in our tested solutions and world-class services and support.
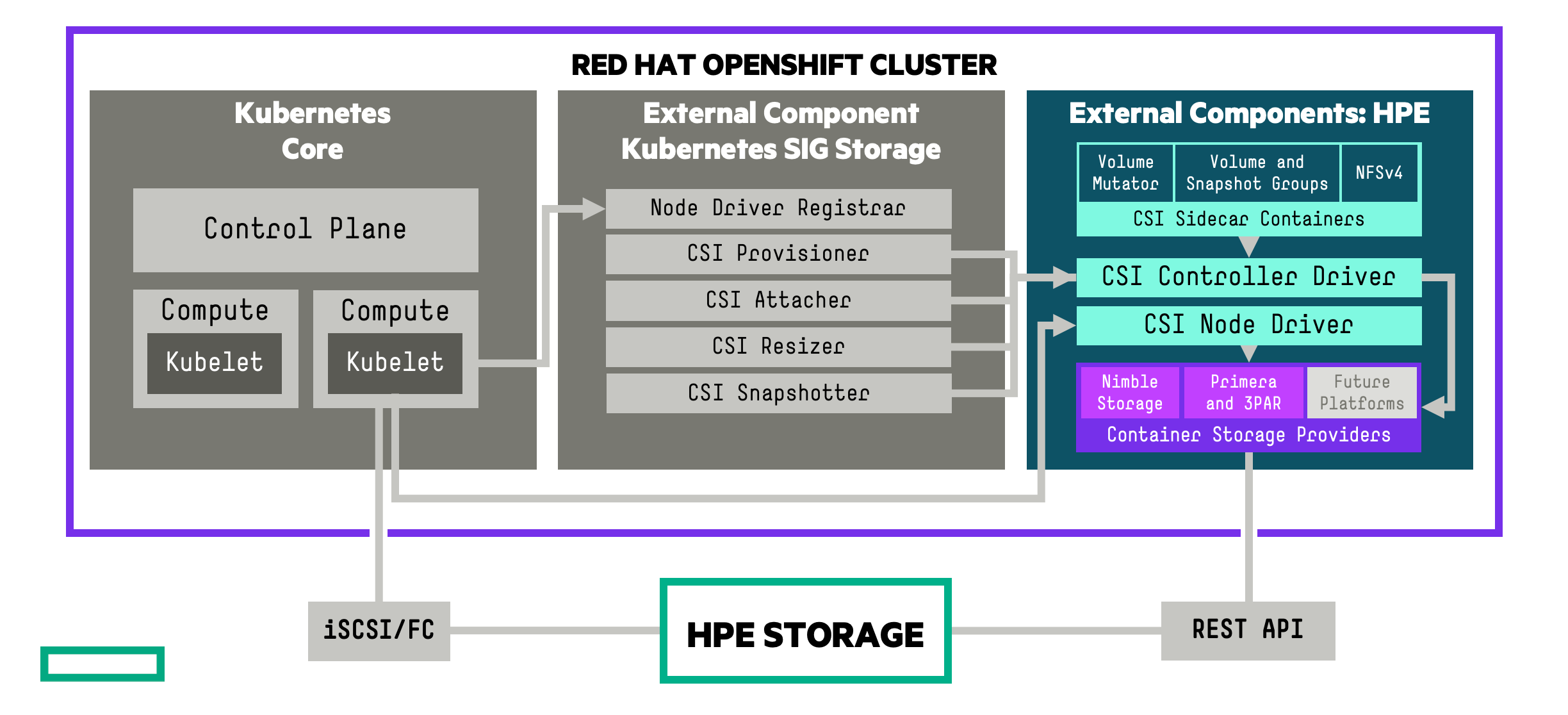
The addition of new capabilities the HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes available in the Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog and deployed from the OpenShift OperatorHub never stops. The HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes has introduced support for HPE Remote Copy Peer Persistence technology for HPE Primera storage systems to protect the data of your mission-critical applications running within the Red Hat OpenShift Container platform and other containerized environments. These features come as part of the upstream HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes that has been developed by HPE and certified by Red Hat.
The HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes is a comprehensive CSI compliant driver per the Kubernetes CSI specification that provides important data management capabilities for containerized workloads, including but not limited to, dynamic provisioning, snapshots, and cloning. Along with the CSI capabilites, the HPE CSI Driver enables HPE storage specific features to be defined within the StorageClass, such as configuring performance policies or protection templates for persistent volumes on HPE Nimble Storage and enabling HPE Remote Copy Peer Persistence for workloads running on HPE Primera.
To learn more about the full capabilities of the HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes check out https://scod.hpedev.io.
Also available are joint Red Hat and HPE Reference Architectures to help customers understand how to build a certified stack using HPE DL/Synergy Servers and HPE storage with OpenShift.
- HPE Reference Architecture for Red Hat OpenShift on HPE ProLiant DL380 Gen10 and HPE ProLiant DL360 Gen10 Servers
- HPE Reference Architecture for Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 4 on HPE Synergy and HPE Storage systems
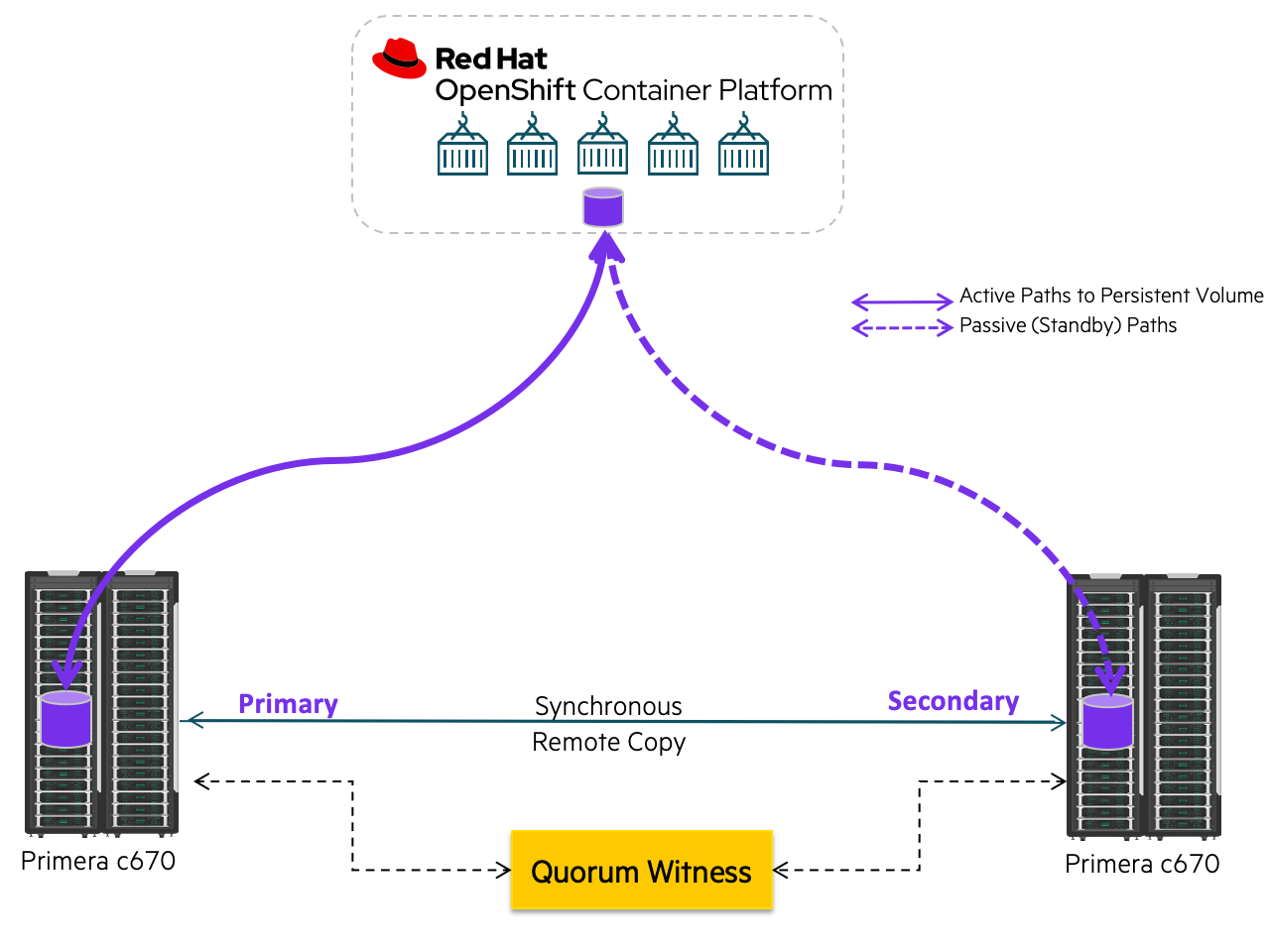
As more and more applications migrate into Kubernetes, it is important to ensure that mission-critical applications using persistent storage are highly available and resilient to failure. The HPE Remote Copy Peer Persistence capability within the HPE CSI Operator coupled with Red Hat's enterprise-grade OpenShift Container Platform provides enhanced availability for your data and transparent failover between sites in the event of a disaster. HPE Primera and 3PAR Remote Copy used in conjunction with Red Hat partners like Kasten by Veeam or Commvault for cluster and application state backup and recovery can serve as the foundation for you disaster recovery strategy for your modern applications.
For information on creating a Remote Copy Peer Persistence configuration, review the HPE Primera Peer Persistence Host OS Support Matrix for the supported host OSs and host persona requirements. Refer to HPE Primera OS: Configuring data replication using Remote Copy over IP for more information.
The following guide is based upon the video Configuring HPE Primera Peer Persistence with HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes on Red Hat OpenShift.
embed YouTube video here
This video goes through many of the steps shown below to configure HPE Remote Copy Peer Persistence with the HPE CSI Operator as well as demonstrates an array failure and how a deployed workload reacts within a Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
- Single zone Kubernetes cluster
- All zoning and Remote Copy links configured (RCIP or RCFC) between sites along with Quorum Witness
- HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes deployed
Here is a guide along with a tutorial video for deploying the HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes within a Red Hat OpenShift cluster.
- HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes deployment on Red Hat Openshift
- Video tutorial: Install the HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes on Red Hat OpenShift
Once the HPE CSI Operatore is deployed, start by creating two Secrets. Configure a Secret for the HPE Primera array located at each site (i.e. default-primera-secret and secondary-primera-secret) that were configured as part of the Remote Copy links.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: default-primera-secret
namespace: hpe-csi-driver
stringData:
serviceName: primera3par-csp-svc
servicePort: "8080"
backend: 10.10.0.2
username: admin_user
password: super_secret_passwordNote: Verify that the Namespace defined within the Secrets is the same as the OpenShift Project name used when deploying the HPE CSI Operator.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: secondary-primera-secret
namespace: hpe-csi-driver
stringData:
serviceName: primera3par-csp-svc
servicePort: "8080"
backend: 10.10.0.3
username: admin_user
password: super_secret_passwordThe next step would be to create a CustomResourceDefinition or CRD to hold the target array information that will be used when creating the replicated volume pairs.
apiVersion: storage.hpe.com/v1
kind: HPEReplicationDeviceInfo
metadata:
name: replication-crd
spec:
target_array_details:
- targetCpg: SSD_r6
targetName: primera-c670
targetSecret: secondary-primera-secret
targetSecretNamespace: hpe-csi-driverWith the Secrets and CustomResourceDefinition available the HPE CSI Driver is now configured and ready to provision replicated volumes.
To get started provisioning replicated volumes, create a replication enabled StorageClass. Specify the CSI sidecars to use the Secret for the default array, define the remoteCopyGroup and the replicationDevices parameters in order to enable replication on volumes using this StorageClass as well as any additional storage parameters as needed. The HPE CSI Driver can use an existing Remote Copy Group or can create a new one based upon the name specified in the StorageClass. During the provisioning process, the volume will be initially created on the primary site array and then the CSI Driver will use the information from the CRD to create the replicated volume on the target site Primera array.
Note: A Remote Copy group is a group of one or more volumes on an HPE Primera array to be replicated to another system. Because the volumes in a Remote Copy group are related, Remote Copy ensures that the data on the volumes within the group maintain write consistency.
For a full list of available StorageClass parameters, see StorageClass Parameters.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "false"
name: replicated-storageclass
provisioner: csi.hpe.com
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: true
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: xfs
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: default-primera-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: hpe-csi-driver
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-publish-secret-name: default-primera-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-publish-secret-namespace: hpe-csi-driver
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-name: default-primera-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-namespace: hpe-csi-driver
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: default-primera-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: hpe-csi-driver
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: default-primera-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: hpe-csi-driver
description: "Volume created using Peer Persistence with the HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes"
accessProtocol: iscsi
cpg: SSD_r6
remoteCopyGroup: new-rcg
replicationDevices: replication-crd
provisioning_type: tpvv
allowOverrides: description,provisioning_type,cpg,remoteCopyGroupNext create a PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) based upon the replicated-storageclass.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: replicated-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 200Gi
storageClassName: replicated-storageclassNext verify the volume has been created successfully and Bound to the cluster
$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
replicated-pvc Bound pvc-ca03a916-a6fb-434c-bc00-6b8 200Gi RWO rep-sc 1mAs the volumes are dynamically created by the HPE CSI Driver and made available to the OpenShift cluster, replication between the default and secondary Primera storage arrays using Remote Copy is transparent to Kubernetes.
Verify the replication status by logging into both Primera arrays to see the sync status of the Remote Copy Group by running showrcopy to verify the replication status.
$ showrcopy
Remote Copy System Information
Status: Started, Normal
Target Information
Name ID Type Status Options Policy
primera-c670 4 IP ready - mirror_config
Link Information
Target Node Address Status Options
primera-c670 0:3:1 10.10.0.3 Up -
primera-c670 1:3:1 10.10.0.3 Up -
receive 0:3:1 receive Up -
receive 1:3:1 receive Up -
Group Information
Name Target Status Role Mode Options
new-rcg primera-c670 Started Primary Sync auto_failover,path_management
LocalVV ID RemoteVV ID SyncStatus LastSyncTime
pvc-ca03a916-a6fb-434c-bc00-6b8 168 pvc-ca03a916-a6fb-434c-bc00-6b8 83 Synced NAThis verifies that volumes have been created on the primary and remote sites and are synchronized within your Kubernetes cluster.
In the case of complete array failure, Remote Copy will protect your mission critical applications and minimize the potential for data loss and downtime. Check out the Peer Persistence video mentioned above to see a demo of what happens to a containerized workload running within OpenShift, when the HPE Remote Copy Quorum Witness detects an array failure and triggers the automatic transparent failover and transitions the workload IO to the secondary site without an outage.
Check out the HPE CSI Operator in the Red Hat Container Catalog. Current supported platforms are HPE Nimble Storage, HPE Primera and HPE 3PAR. Sign up to the HPE DEV Slack community at slack.hpedev.io (or login at hpedev.slack.com if you already have signed up) to chat with the HPE staff, partners and customers. Also stay informed via our announcements and updates, we hang out in #kubernetes, #nimblestorage and #3par-primera.
- Learn how to install the HPE CSI Operator on HPE Storage - Container Orchestrator Documentation (SCOD) portal
- Learn more about HPE Nimble Storage, HPE Primera and HPE 3PAR at hpe.com/storage
- Join the HPE Developer Community to learn from other HPE developers who use HPE products