This gist was made on a Ubuntu 18.04 LTS.
A. Default OpenJDK - installed on your local machine
B. Oracle SQL Developer - Linux RPM installed on your local machine
C. Oracle DB instance hosted on AWS using RDS
D. Remote connection to your DB using Oracle SQL Developer
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt install default-jdk
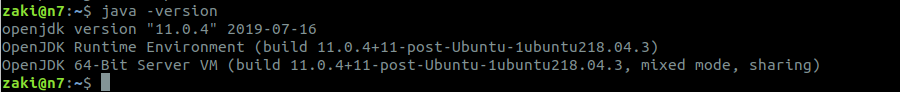
$ java -versionGo to https://www.oracle.com/database/technologies/appdev/sql-developer.html > download
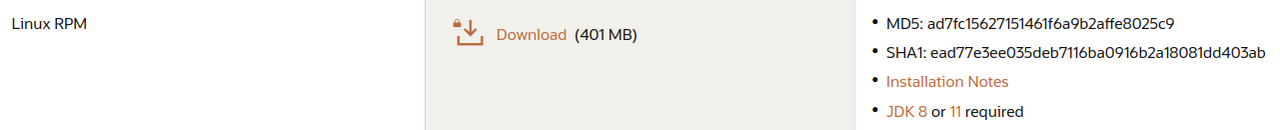
To Linux RPM click on Download.
Open your Terminal, create a folder oracleSQL and move the "sqldeveloper-19.2.1.247.2212.noarch.rpm" file you've downloaded in that folder.
Alien converts an RPM package file into a Debian package file or Alien can install an RPM file directly.
Open a new Terminal window, and use as follows:
sudo add-apt-repository universe
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install alienGo to your oracleSQL folder, and use as follows:
sudo alien <name_of_package>.rpm (e.g: I'm using sqldeveloper-19.2.1.247.2212.noarch.rpm).
Once command completed...
$ ls
$ sudo dpkg -i <name_of_package>.debYour directory should now look like this ...
The executable should be located in the opt/sqldeveloper ...
$ ./sqldeveloper.shIf you have an
AWS,AzureorGCPaccount, you can connect to your database using Oracle SQL Developer.
I'm here using an Oracle RDS instance on my AWS account.
On your AWS Management Console, go to Services > RDS.
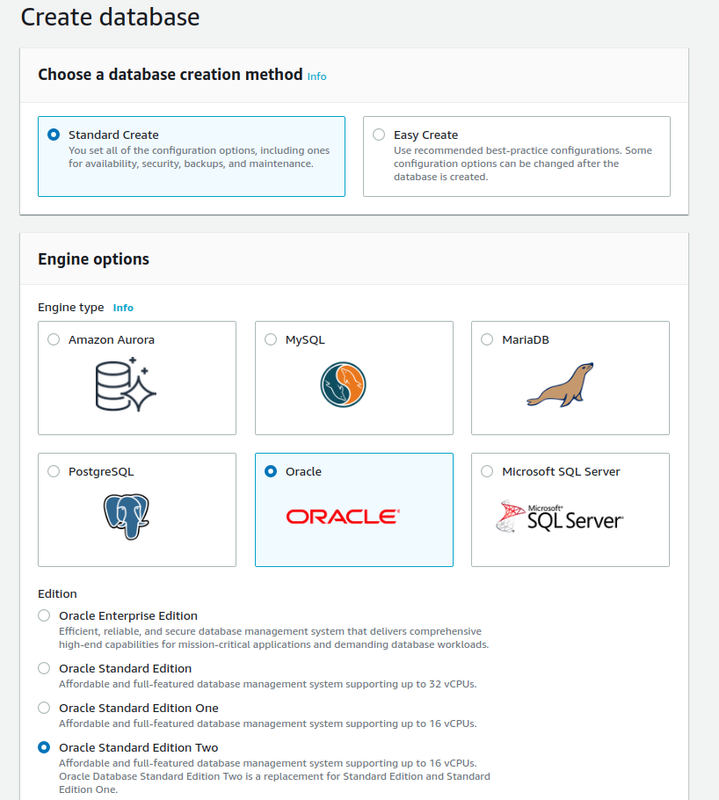
Go to Databases > Create database > Choose Standard create > Configuration: Oracle as engine type
Edition: choose Oracle Standard Edition Two
Version: select Oracle 12.1.0.2.v2
Templates: choose Dev/Test
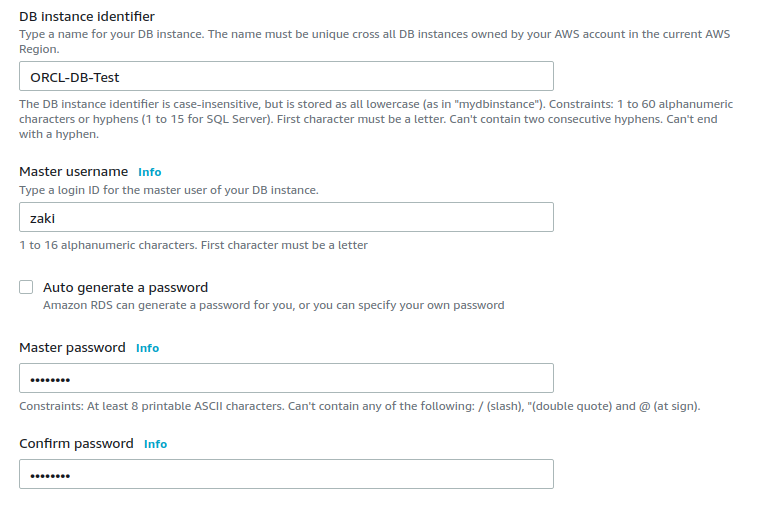
DB instance identifier: ORCL-DB-Test
Master username: choose a username
Master password: choose a password
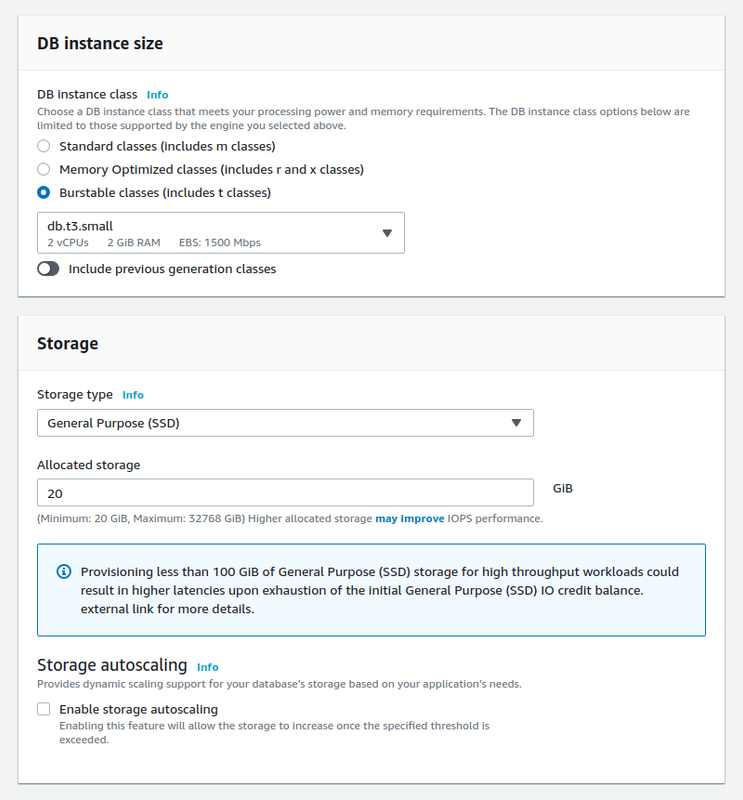
DB instance size: choose Burstable classes > select db.t3.micro
DB instance size: select Burstable classes (includes t classes) > db.t3.small
Storage > Allocated storage: 20 GiB
Disable "storage Auto Scaling"
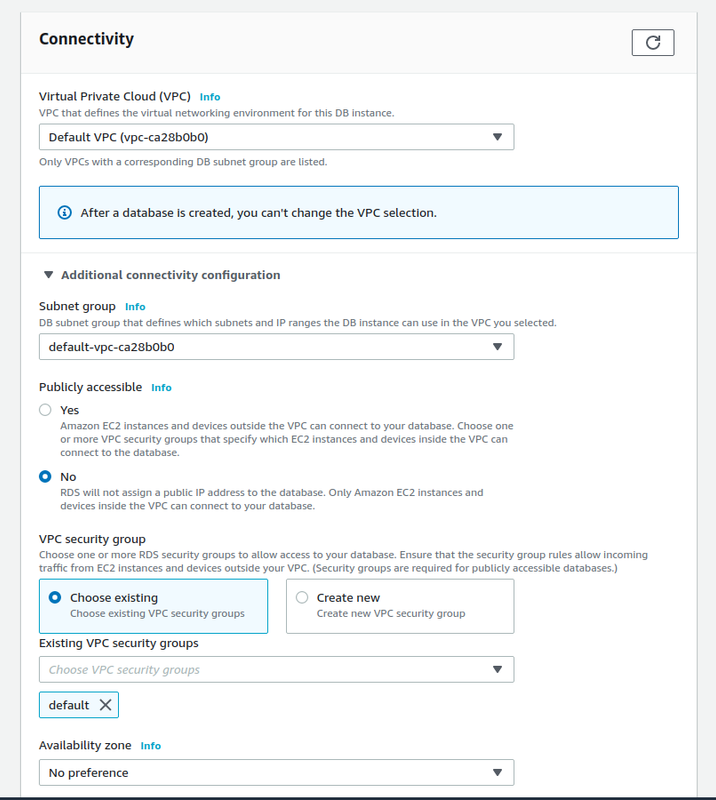
Connectivity: set Publicaly accessible to Yes
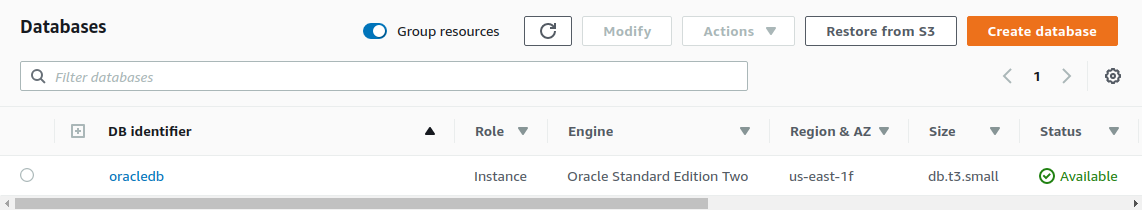
Then Create database. When your DB is up and running...
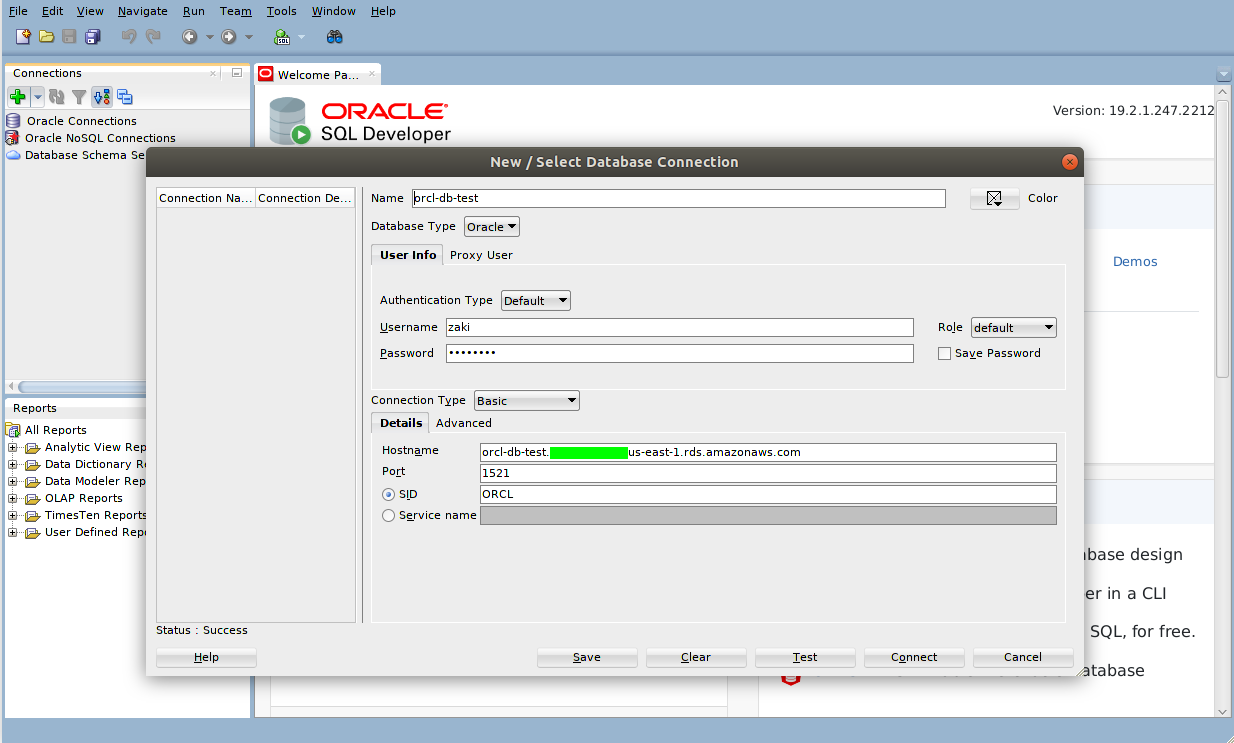
Go back to Oracle SQL Developer locally and connect to your DB credentials.
On Connections click on the "plus" button.
Connect with the information provided upon the DB creation on RDS.
Here you go! You are now connected to your Oracle DB remotely using Oracle SQL Developer.
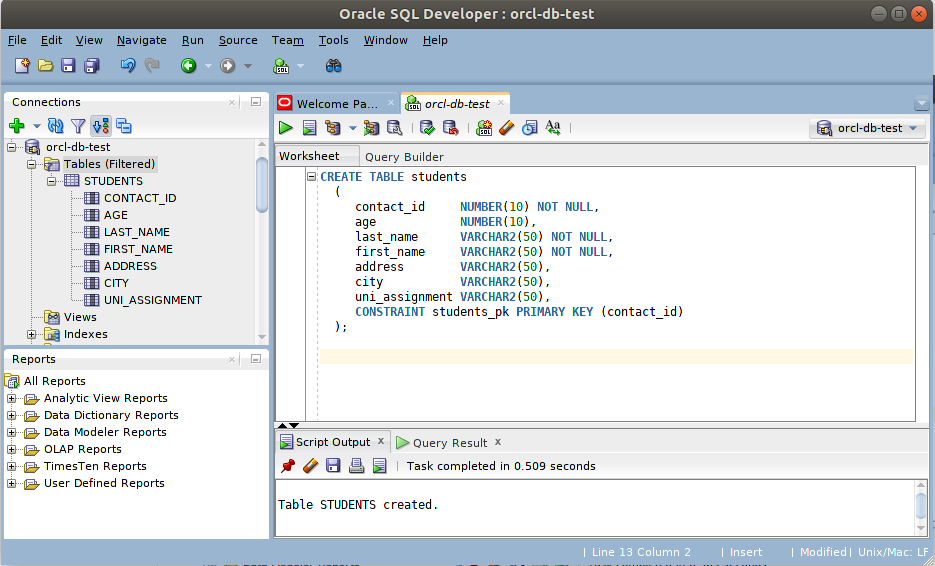
In your left panel, you are connected to a database. Now you can create tables and start interracting with your DB.
We are here using basic SQL syntax to show how our DB works.
CREATE TABLE students
(
contact_id NUMBER(10) NOT NULL,
last_name VARCHAR2(50) NOT NULL,
first_name VARCHAR2(50) NOT NULL,
address VARCHAR2(50),
city VARCHAR2(50),
uni_assignment VARCHAR2(50),
CONSTRAINT students_pk PRIMARY KEY (contact_id)
); You can create and provision tables in Oracle DB using PL/SQL syntax for more advanced needs.
If you enjoyed this gist, feel free to fork and share it! Thanks.
- Isaac Arnault - Start with Oracle SQL Developer on Linux.




Really helped me. Thank you.