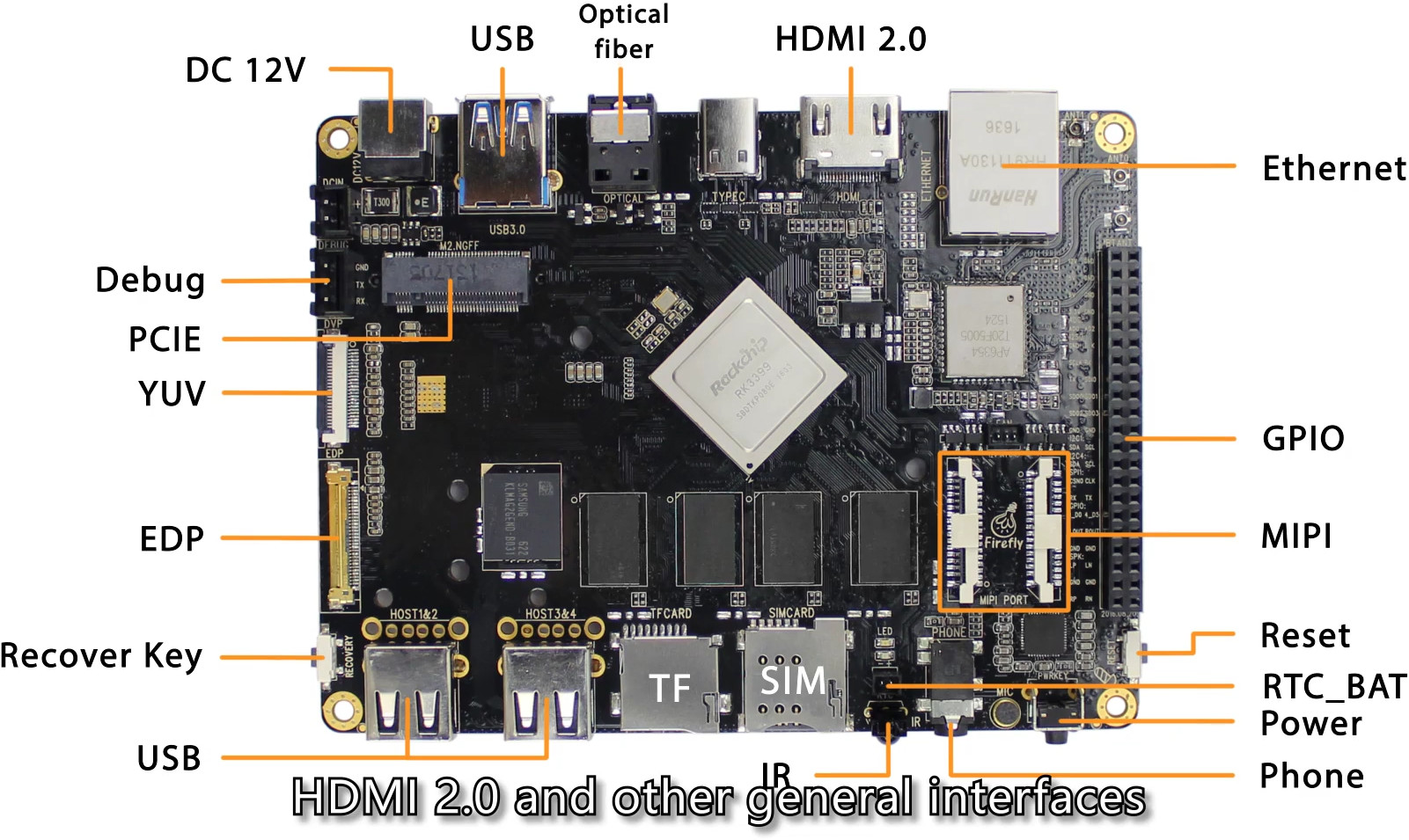
I bought the basic Firefly RK3399 from Amazon for $130. It has 2GB RAM and 16 GB eMMC. There is an advanced version with 4GB RAM, but cost more $199.
The default OS doesn't have OpenCL support. The easy way is downloading an image with OpenCL, namely libOpenCL.so pre-installed and then flash into the board.
- Download a Ubuntu 16.04 image from Google Drive.
- Extract the download 7z file to get a 2.2 GB image
Firefly-RK3399_xubuntu1604_201711301130.img. - Flash the image by following this document. (Username firefly, password: firefly)
In particular, if you have a Linux desktop, then we can use the upgrade_tool_v1_26.tar provided in this repo. (Note: : the other two linux tools rkflashkit and rkflashtool do not support flash the whole image. )
-
Cut off the power of the board
-
Connect it to the linux host machine with provided usb cable, and use the provided type-c converter to connect to the board
-
Press the RECOVERY key, next power on, and then release the key after around two second.
-
Install
upgrade_toolby:tar -zxvf upgrade_tool_v1_26.tar sudo chown root:root upgrade_tool sudo chmod +x upgrade_tool sudo cp upgrade_tool /usr/local/bin
Then run
upgrade_toolyou will see the board is connected -
Flash the image by
sudo upgrade_tool uf Firefly-RK3399_xubuntu1604_201711301130.img
Reboot the board then you will login into the Ubuntu automatically.
But note that this image only ships a libOpenCL.so, if you want to compile OpenCL program on the board, you need to install the header files, which is provided in opencl-header.tar.gz, just extract it into a proper directory such as
sudo tar -zxvf opencl-header.tar.gz -C /usr/include/We can check if the opencl driver works properly by using the benchmark tool clpeak
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install cmake git
git clone https://github.com/krrishnarraj/clpeak && cd clpeak
cmake . -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=g++ && make
./clpeakIf everything works well, then you probably will see the following outputs:
Platform: ARM Platform
Device: Mali-T860
Driver version : 1.2 (Linux ARM)
Compute units : 4
Clock frequency : 200 MHz
Global memory bandwidth (GBPS)
float : 3.17
float2 : 6.07
float4 : 7.88
float8 : 6.55
float16 : 6.26
Single-precision compute (GFLOPS)
float : 25.09
float2 : 45.51
float4 : 46.22
float8 : 41.67
float16 : 46.40
half-precision compute (GFLOPS)
half : 23.11
half2 : 50.19
half4 : 98.30
half8 : 93.48
half16 : 93.94
Double-precision compute (GFLOPS)
double : 3.59
double2 : 3.30
double4 : 20.97
double8 : 20.65
double16 : 20.39
Integer compute (GIOPS)
int : 20.15
int2 : 49.64
int4 : 47.12
int8 : 49.17
int16 : 41.47
Transfer bandwidth (GBPS)
enqueueWriteBuffer : 4.61
enqueueReadBuffer : 2.60
enqueueMapBuffer(for read) : 475.11
memcpy from mapped ptr : 2.50
enqueueUnmap(after write) : 2790.39
memcpy to mapped ptr : 1.92
Kernel launch latency : 190.64 us
Follow the cross complication tutorial to compile the runtime on RK3399, and local TVM.
Follow deploy pretrained model on Mali to run Resnet-18 on RK3399. To benchmark the performance, we can append the following code block:
import time
ntimes = 10
tic = time.time()
for _ in range(ntimes):
module.run()
ctx.sync()
print((time.time()-tic)/ntimes)