In this tutorial, I will be going over to how to deploy a Javascript app from start to finish using AWS and EC2. Recently, my partner Tu and I launched our app AlgoAcademy (a resource for reviewing algorithms and data structures) and we wanted to share with other developers some of the lessons we learned along the way.
Following this tutorial, you will have an application that has:
-
A React frontend, Express backend
-
An AWS EC2 server configured to host your application
-
SSL-certification with Certbot
-
A custom domain name
-
Continuous deployment with Github Actions/SSM Agent
We have provided a dummy repo to follow along with here, but feel free to apply it to your own application as necessary.
Here is the project layout:
mern-app
|__ client/ (React App Frontend)
| |__ public/
| |__ src/
|__ scripts/
|__ app.js (Express Backend)
|__ package.json
|__ Dockerfile
|__ docker-compose.yml
Start by cloning the project with the command:
$ git clone https://github.com/rmiyazaki6499/mern-app.git
To make this as easy as possible, we will be using Docker Compose to creat our container.
-
If you do not have Docker yet, start by downloading it if you are on a Mac or Windows: https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop
-
Or if you are on a Linux Distribution follow the directions here: https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/
-
To confirm you have Docker Compose, open up your terminal and run the command below:
$ docker-compose --version docker-compose version 1.26.2, build eefe0d31 -
Go into the project directory to build and run the container with:
$ cd mern-app/ $ docker-compose up --build -
Navigate to http://localhost:5000, you should see something like this:
-
To stop the container from running, use
<Ctrl-C>twice. -
To close down the container use the command:
$ docker-compose down -
Then to clean up the container and image which we are no longer using use the command:
$ docker system prune -fa -
Confirm that the container and image is no longer there with:
$ docker system df -v
To preview the project on your local machine, follow the directions below.
-
Install dependencies for both Express and React:
$ cd mern-app/ $ npm install $ cd client/ $ npm install -
To run the React server, use this command in the client directory:
$ npm start -
If you go to http://localhost:3000, you should see something like this:
The API call is not working yet because we have not started the Express server. In another terminal session, run the command "npm start" at the root directory of the project.
Express is now running on port 5000. Switch back to the window with http://localhost:3000 and refresh the page. You should see an updated message at the bottom:
We now have two servers running: one for the React frontend and one for the Express backend. For this tutorial, however, we only need one server running, so we will run a reverse proxy for React and have Express serve all the content. Stop the React server on port 3000 with Ctrl-C.
-
In the
clientdirectory run the command:$ npm run-script buildReact will create a production build of your app which serves as an entry point for the static content (HTML, CSS, and Javascript). Now, if you go to http://localhost:5000, you should see the same React page from earlier!
This project currently will only display locally, so in order for anyone on the internet to see it, we will need a remote computer to serve our app.
Why choose AWS?
-
It offers a lot of free services for new accounts.
-
Very popular among startups and even enterprises.
-
Customer service support, in our opinion, is a step above the competition.
-
If you do not have an account, check out this step by step guide by Amazon here.
Before you provision a new server, it is best practice to make sure your account is as secure as possible by following the prompts on your Security Status checklist. This can be found under the IAM tab from your console's homepage.
Amazon's EC2 or Elastic Compute Cloud is one of the core products/services AWS provides and is the main building block for many of AWS's other services. It allows users to essentially rent virtual computers on which to run their own applications. You can learn more about EC2 here.
Start out by going into the AWS Console and going to the EC2 tab. An easy way to get there is through the Services link at the top and search for EC2 in the prompt.
We recommend setting your AWS Region to the one closest to you or your intended audience. However, please note that not all AWS Services will be available depending on the region. For our example, we will be working out of the us-east-1 as this region supports all AWS Services.
You should see this screen (as of July 2020):
Go to the Running Instances link on the EC2 dashboard and click Launch Instance.
In this step, AWS will prompt you to choose an AMI. AMI's are templates to configure new instances. For this tutorial, we will be using Ubuntu 18.04 64-bit (free tier).
Next, select the t2.micro instance type.
On the next screen, keep clicking next until you see the option to Configure Security Group.
Security groups are virtual firewalls for your instances.
Important: by default, there is an implicit deny on all ports meaning if you do not add rules, all incoming/outgoing traffic is blocked. Security groups are also stateful, which means setting inbound rules for a certain port will also affect the outbound rules for that port.
Set your Security Group settings with the following:
Setting Anywhere on Source for Custom TCP will display a warning flag, but you can ignore that for this tutorial. Ideally, you only want to set known IP addresses.
| Type | Port Range | Description. |
|---|---|---|
| SSH | 22 | Port for SSH'ing into your server |
| HTTP | 80 | Port for HTTP requests to your web server |
| HTTPS | 443 | Port for HTTPS requests to your web server |
| Custom TCP | 5000 | Port which Express will run |
| Custom TCP | 27017 | Port at which to connect to MongoDB |
As you can see with the warning near the bottom of the screen, you do not want to set your SSH Source IP as anywhere. This will create a security vulnerability as anyone can try to attempt to log into your server.
Therefore, be sure to set it to your own IP address and any other IP address which may need access to the instance.
Click forward to Review and Launch to view all configurations of your Instance/AMI. If the configurations look correct go ahead and hit Launch.
Once you launch the instance, AWS will prompt you to create a key pair. A key pair consists of a public key that AWS stores and a private key file that you store. Together they allow you to connect to your instance securely through asymmetrical encryption.
If this is the first time you are creating a key pair for your project, select Create a new key pair from the drop-down and add a name for the key pair.
Be sure to store the key pair in a secure location. It is generated only once and AWS will not have access to it if you lose it. This is your only means to log into the EC2 instance via SSH.
Once you have downloaded the key pair make sure to move the .pem file to the root directory of your project on your local computer.
Next, check the checkbox acknowledging that you have access to the private key pair and click Launch Instances. This should take you to the Launch Status page.
Click on the Instances tab on your EC2 console.
The instance may take a couple of minutes to launch. Once it passes its' status checks, the instance state should show a green circle and a "running" state.
Before you can log into your EC2 instance, it is important to first generate an Elastic IP and associate it to your EC2 instance.
An Elastic IP is a dedicated IP address for your EC2 instance. Although the instance has a public IP address assigned upon creation, that IP address is dynamic and does not persist if you stop and start the instance. With an Elastic IP address, you can mask the failure of an instance by remapping the address to another instance in your account.
Therefore, by using an Elastic IP, you can have a dedicated IP to which users from the internet can access your instance. This will come in handy later when you assign a custom domain name and add SSL certification to the server.
Note: If you are using the free tier, AWS will charge you if your Elastic IP is NOT associated with an AWS identity.
On the EC2 dashboard, look under the Network & Security tab and go to Elastic IPs:
It should take you here:
Click on Allocate Elastic IP address.
It should take you here:
Select Allocate.
This should create an Elastic IP. The next step is to associate that Elastic IP to the instance.
With the Elastic IP checked on the left side:
-
Go to Actions
-
Click on Associate Elastic IP address
-
Make sure your Resource type is Instance
-
Search for your instance (if this is your first time, it should be the only one)
-
Click Associate
To check if everything is done correctly, go to the Instances tab and in the instance details, you should see the Elastic IP.
With the instance selected in the EC2 console, click Connect near the top. You will be prompted with directions on how to connect to your EC2 instance:
-
Changing the .pem file's permission to read-only ensures nobody can modify your private key.
Once you are logged into your server, use the following script to install all of the project dependencies:
curl https://gist.githubusercontent.com/cornflourblue/f0abd30f47d96d6ff127fe8a9e5bbd9f/raw/e3047c9dc3ce8b796e7354c92d2c47ce61981d2f/setup-nodejs-mongodb-production-server-on-ubuntu-1804.sh | sudo bash
This will install the following:
-
Node.js 10.x & NPM
-
MongoDB 4.0
-
PM2
-
NGINX
-
UFW (Firewall)
*Note: If you would like to better understand what is going on in this script please check out his blog here.
Recall the steps earlier we did with the dummy project on our local machine. We will repeat that on the EC2 instance.
% git clone https://github.com/rmiyazaki6499/mern-app.git
% cd mern-app/
% npm install
% cd client/
% npm install
% npm run-script build (or npm build if you have that set up)
PM2 is a daemon process manager for Node.js applications that manages and keeps applications online. To take a look at our current PM2 processes, use the command:
% sudo pm2 status
You can see that we do not have any processes running yet. At the root of your project directory with our Express app run:
% sudo pm2 start app.js
Note: We are using app.js for our app but yours may use server.js.
To stop Express, use:
% sudo pm2 stop app.js
Once you have stopped it, start Express again, this time with flags.
% sudo pm2 start app.js -i max --watch
-
-i max- allows us to run processes with the max number of threads available. Because NodeJS is single-threaded, using all available cores will maximize the performance of the app. -
--watch- allows the app to automatically restart if there are any changes to the directory. You can think of it as similar to the package nodemon but for production.
Next, we need to configure NGINX to redirect web traffic. The goal is to have API endpoints go through Express and have React code serve the rest.
Create a new NGINX config file with the following command:
% sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/<YOUR-PROJECT-NAME>
Paste in the following configurations and replace any of the ALL CAPS sections with your own project details:
server {
server_name <YOUR EC2 ELASTIC IP ADDRESS>;
# react app & front-end files
location / {
root /home/ubuntu/<YOUR PROJECT DIRECTORY>/client/build/;
try_files $uri /index.html;
}
# node api reverse proxy // the /api/ is assuming your api routes start with that i.e. www.your-site.com/api/endpoint
location /api/ {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_pass http://localhost:5000;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
Important:
-
The root line in
location/needs to be where the static files are served. In this case, it is in the client's build directory. For the follow-along, it would behome/ubuntu/mern-app/client/build/. -
The proxy_pass in location /api needs to be the location of where Express is running (in this case localhost:5000, but it can be different depending on your configuration). Once your NGINX config is set up, make sure there are no syntax errors with:
% sudo nginx -tNext, create a soft link of your config file from sites-available to the sites-enabled directory. This step is important because NGINX will use the configuration settings located at /etc/nginx/sites-available/default by default if there is nothing in sites-enabled.
% sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/<YOUR-PROJECT-NAME> /etc/nginx/sites-enabledRestart the NGINX Web Server with:
% sudo systemctl restart nginxNow if you go to your Elastic IP on your browser it should show the app!
Continuous Deployment is helpful because it saves you the time of having to ssh into your EC2 instance each time you make an update on your codebase.
In this project, we will be using a Github Action called AWS SSM Send-Command created by peterkimzz to implement auto-deployment.
Github Actions is a service by Github that allows you to perform actions such as run scripts every time something happens to a repository. In our case, we will run a script to install the latest dependencies and restart our server every time a push is made to master.
For Github Actions to work, it needs a way to communicate with the EC2 Instance and vice-versa. In order to do that, we need to assign permissions via IAM roles.
To create an IAM Role with AmazonSSMFullAccess permissions:
-
Open the IAM console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/.
-
In the navigation panel, select Roles, and then click Create role.
-
Under Select type of trusted entity, choose AWS service.
-
In the Choose a use case section, choose EC2, and then choose Next: Permissions.
-
On the Attached permissions policy page, search for the
AmazonSSMFullAccesspolicy, choose it, and then choose Next: Review. -
On the Review page, type a name in the Role name box, and then type a description.
-
Choose Create role. The system returns you to the Roles page.
Once you have the Role created:
-
Go to the EC2 Instance Dashboard
-
Go to the Instances link
-
Highlight the Instance
-
Click on Actions
-
Instance Settings
-
Attach/Replace IAM Role
-
Select the SSM Role you had created earlier
-
Hit Apply to save changes
With our instance being able to use the SSM Agent, we will need to provide it some details so that it can access our EC2 instance.
Now that the instance is able to communicate to Github via SSM Agent, you will need to provide the repo with credentials. Github Secrets act like environment variables for repositories and store sensitive data such as AWS login information. In order for the Github Actions script to work, it needs these three secrets: AWS_ACCESS_KEY, AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, and INSTANCE_ID.
There is an article by AWS on how to find your AWS Access Key and Secret Access Key here. Your instance ID is shown on your instances tab under EC2.
Start by going to your Github project repo:
- Then go to your Settings
- On the menu on the left, look for the link for Secrets
- There, add the three Secrets with these keys:
-
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID -
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY -
INSTANCE_ID
-
Next, let's create a bash script to download dependencies and restart NGINX and PM2. Inside the EC2 instance, create a deploy.sh script in the root of the directory:
% vim deploy.sh
Paste in the following commands:
#!/bin/sh
sudo git pull origin master
sudo npm install
cd client
npm install
sudo npm run-script build
cd ..
sudo systemctl restart nginx
sudo pm2 restart all
AWS SSM Send-Command requires a .yml file to execute. At the root of the project, create these two directories:
% mkdir -p .github/workflows/
Create a new YAML file with:
% sudo vim .github/workflows/deploy.yml
Paste in the following:
name: Deploy using AWS SSM Send-Command
on:
push:
branches: [master]
jobs:
start:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: AWS SSM Send Command
uses: peterkimzz/aws-ssm-send-command@1.0.1
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: us-east-1
instance-ids: ${{ secrets.INSTANCE_ID }}
comment: Deploy the master branch
working-directory: /home/ubuntu/<YOUR PROJECT DIRECTORY>
command: /bin/sh ./deploy.sh
```
The Secrets we provided to the repo earlier comes into use in this script.
There are 3 parts of the .yml file to configure:
1. The aws-region should be the same region as where you have created your EC2 instance. (If you do not know, check the top left of your EC2 console to confirm the region you are in).
2. working-directory should be the directory where you created the deploy.sh script.
3. command should be the command you would like the SSM agent to run.
Once this is complete, commit and push the workflow to your repo.
---
## Setting up your Domain
So far, users can access the site using the Elastic IP. However, it can be difficult to remember and share so we will configure a custom domain name.
To get started, you need to first purchase a domain. This can range from $10 to $1,000+s. Amazon has a service called Route53 you can use or you can choose other providers such as [Google Domains](https://domains.google/), [GoDaddy](https://www.godaddy.com/), etc. (we used Google for AlgoAcademy which was $10/year).
There are two steps you would need to configure to connect the project with a custom domain:
- Create domain records with DNS registrar
- Configure NGINX on the EC2 instance to recognize the domain
---
### _Creating Domain records_
Let's start with configuring our DNS with records:
- Go to the **DNS** portion of your registrar.
- Find where you can create custom resource records.
Set the records like so:
| Name | Type | TTL | Data |
| ---- | :---: | :-: | ----------------------: |
| @ | A | 1h | YOUR-ELASTIC-IP-ADDRESS |
| www | CNAME | 1h | your-awesome-site.com |
### _Configuring our Web Server_
Edit the NGINX config file inside your EC2 instance:
% sudo vim /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
Update the `server:server_name` section of the config file:
server { server_name your-awesome-site.com www.your-awesome-site.com; ...
Save and restart NGINX:
sudo sudo systemctl restart nginx
*DNS changes can take up to 48 hours to update so your results may vary. Once it is complete, going to your custom domain should redirect you to your app.*
---
## HTTPS
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a server and a client. So far, we have been serving web content over HTTP, which can be dangerous as data sent between the server and client is not encrypted. If you are handling user sign-in and need to protect data such as passwords or credit card information, it is always best practice to have SSL certification on your applications.
In this tutorial, we will be using Certbot by letsencrypt.org, a non-profit organization that provides free SSL Certificates.
---
### _Installing Certbot_
On your browser go to https://certbot.eff.org/instructions.
Select the Software and Operating System (OS) you are using. In this case, we are using NGINX and Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (bionic).
Inside your EC2 Instance, follow the command-line instructions until you see these instructions:
% sudo certbot --nginx
After running this command, Certbot will present to you the following prompt: Which names would you like to activate HTTPS for?
If NGINX is configured correctly, it should show both your root domain as well as with the www subdomain:
1: your-awesome-site.com 2: www.your-awesome-site.com
Select enter to activate both HTTP and HTTPs. The next prompt will be:
Please choose whether or not to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS, removing HTTP access.
1: No redirect - Make no further changes to the web server configuration. 2: Redirect - Make all requests redirect to secure HTTPS access. Choose this for new sites, or if you're confident your site works on HTTPS. You can undo this change by editing your web server's configuration.
Select option 2 as this will redirect all traffic through HTTPS and is the most secure option. Afterward, Certbot will make changes to the NGINX configuration file.
*Note: Once your site is using HTTPS, double-check your API calls and make sure that they are going to the https:// endpoint rather than http://. This may be an unnecessary precaution, but it is an easy bug to miss.*
Next, go to your custom domain. Check to see if there is a lock icon next to your URL.
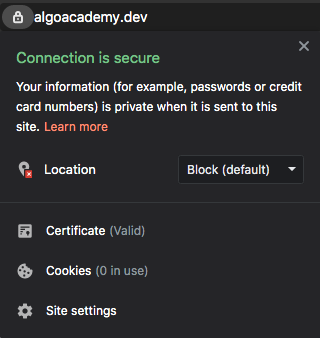
Congratulations! You have successfully deployed a web app with HTTPS!
---
## Closing Thoughts
I hope this provided some help for those getting started with web development and AWS. If you run into any problems, please feel free to reach out to either me or [Tu](https://github.com/tuvo1106/tuvo1106) and we can try our best to help. Thank you for reading!
[Back to Table of Contents](#table-of-contents)

















I think the problem is routing within docker search for how docker handles routing: