NoSQL DB is a database used to manage huge sets of unstructured data, where the data is not stored in tabular relations like relational databases.
Following are the NoSQL database types:
- Document databases: In this type, key is paired with a complex data structure called document. Example: MongoDB;
- Graph stores: This type of database is ususally used to store networked data. In this type of NoSQL DB we can relate data based on some existing data.
- Key-value stores: These are the simplest NoSQL databases. In this each document is stored with a key to identify it. It is used to save data in a type known today as dictionary or hash table. Dictionaries contain a collection of objects, or records, which in turn have many different fields within them, each containing data. These records are stored and retrieved using a key that uniquely identifies the record, and is used to quickly find the data within the database. The most popular implementation of a key-value database is Redis.
- Wide-column stores: It uses tables, rows, and columns, but unlike a relational database, the names and format of the columns can vary from row to row in the same table. Example : Cassandra (used in Facebook), HBase etc.
:::info MongoDB:
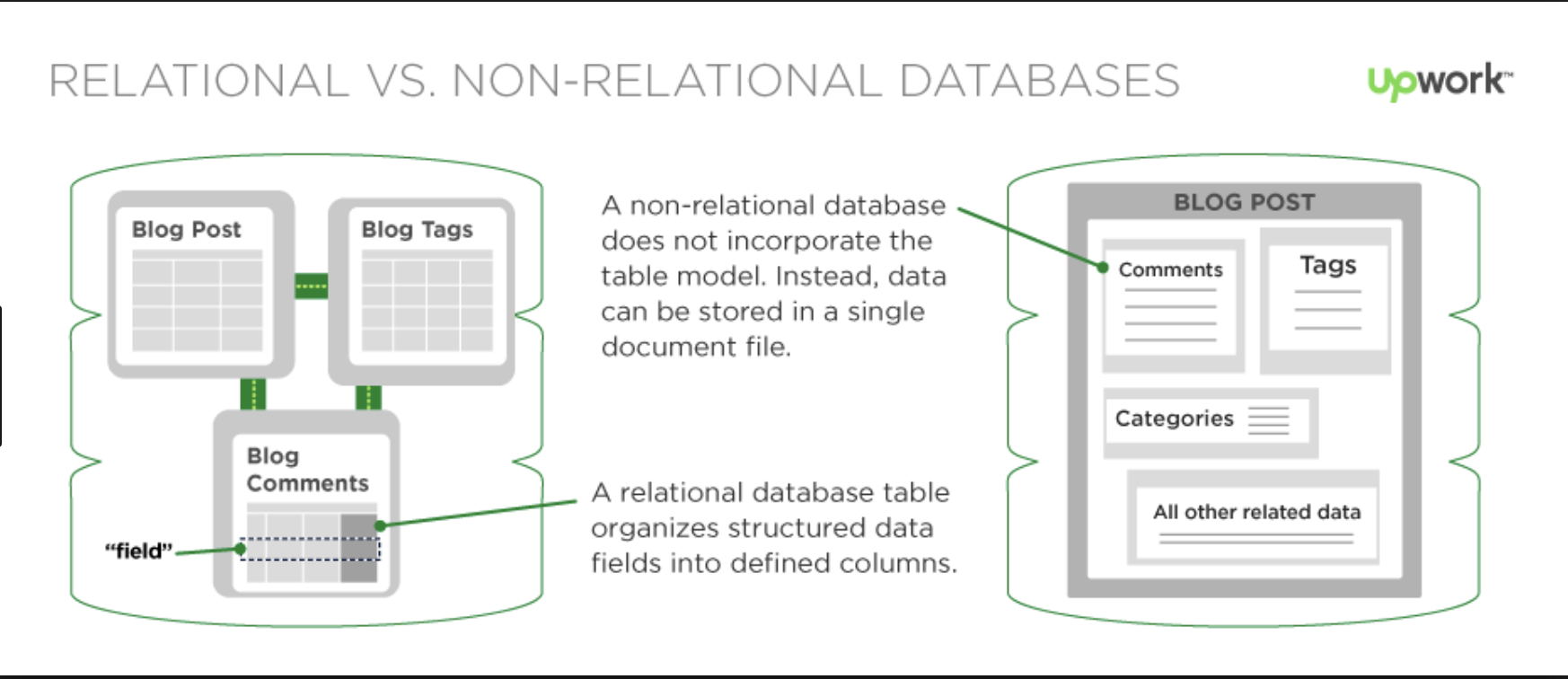
- is a document oriented database that stores data in collections instead of tables; collection is nothing but a set of documents; being schemaless, any type of document can be saved in a collection (although similarity is recommended);
- is a NoSQL database which stores the data in form of key-value pairs (like in JSON). :::
Most of the currently existing relational databases have failed in solving some of the complex modern problems like:
- Continuosly changing nature of data - structured, semi-structured, unstructured and polymorphic data.
- Applications now serve millions of users in different geo-locations, in different timezones and have to be up and running all the time, with data integrity maintained
- Applications are becoming more distributed with many moving towards cloud computing.
NoSQL plays a vital role in an enterprise application which needs to access and analyze a massive set of data that is being made available on multiple virtual servers (remote based) in the cloud infrastructure and mainly when the data set is not structured. Hence, the NoSQL database is designed to overcome the Performance, Scalability, Data Modelling and Distribution limitations that are seen in the Relational Databases.
Structured data is usually text files, with defined column titles and data in rows. Such data can easily be visulaized in form of charts and can be processed using data mining tools.
Unstructured data can be anything like video file, image file, PDF, Emails etc. What does these files have in common, nothing. Structured Information can be extracted from unstructured data, but the process is time consuming. And as more and more modern data is unstructured, there was a need to have something to store such data for growing applications, hence setting path for NoSQL.
The major difference between MongoDB and SQL Databases is the way they handle data. In SQL databases, data is stored in form of traditional 2 dimensional row-column structure while in MongoDB rich data document model is followed, which allows storage of any type of data.
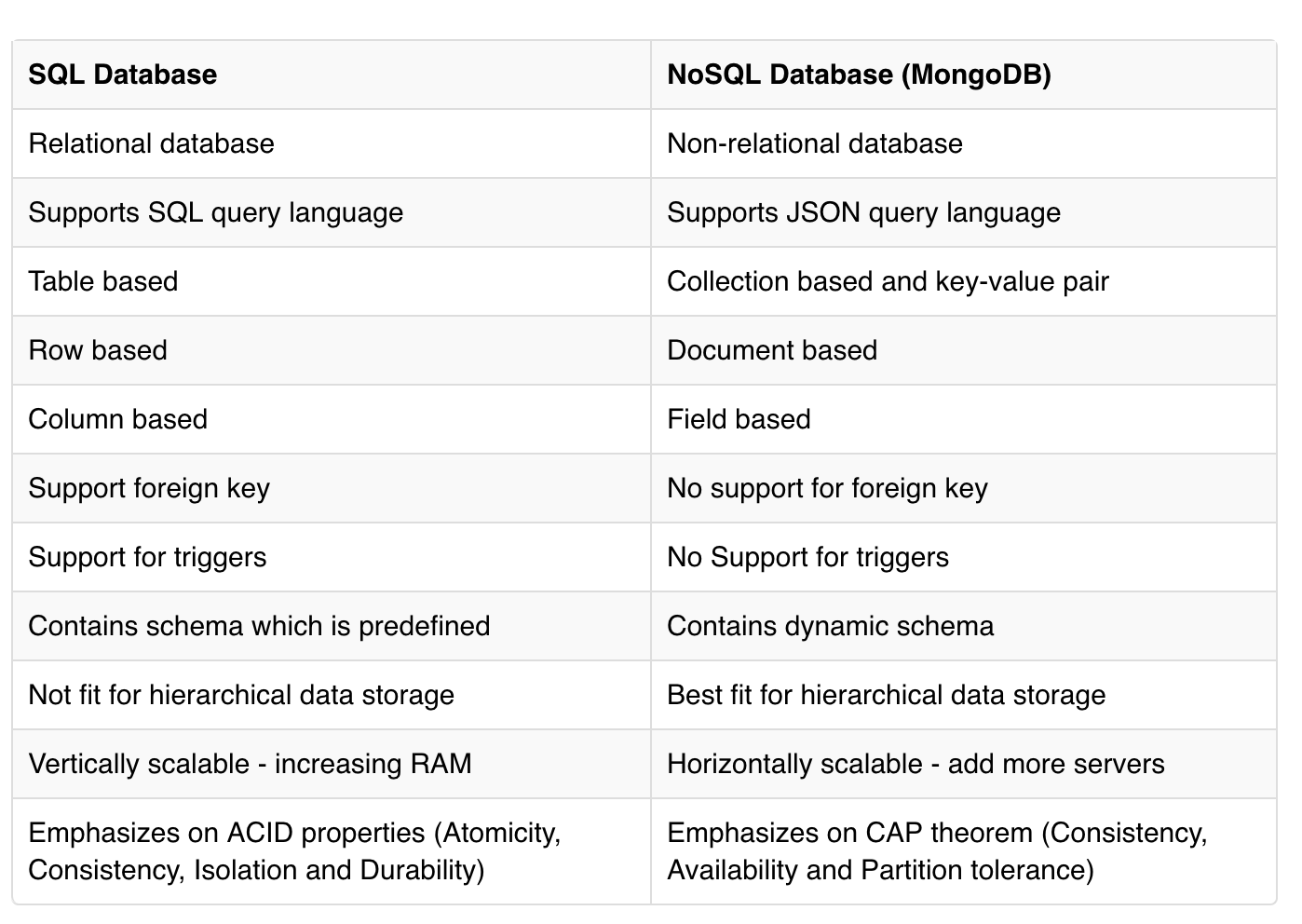
Let us see some of the key differences between MongoDB and other SQL databases:
Additional explanation:
- MongoDB doesn't support foreign key: We can define the so-called foreign key in MongoDB. However, we need to maintain the data integrity BY ourselves. For example:
student
{
_id: ObjectId(...),
name: 'Jane',
courses: ['bio101', 'bio102'] # <= ids of the courses
}
course
{
_id: 'bio101',
name: 'Biology 101',
description: 'Introduction to biology'
}The courses field contains _ids of courses. It is easy to define a one-to-many relationship. However, if we want to retrieve the course names of student Jane, we need to perform another operation to retrieve the course document via _id. This process is not automated, as well as if some of the courses gets removed, we need to perform another operation to update the courses field in the student document.resource
-
MongoDB doesn't support triggers
To learn more about triggers, visit this online resource.
-
MongoDB is the best fit for hierarchical data storage: read more here.
One of the best adventages of the MongoDB:
MongoDB documents also align with the structure of objects in modern programming languages, as they are a form of JSON. This makes it easy for developers to map the data used in the application to its associated document in the database. While in SQL Database, creating a table with columns mapped to the attributes of an object in programming language, appears a little tedious.
Here we will be discussing some of the main advantages of NoSQL databases with examples.
- Dynamic Schemas In Relational Databases like MySQL, we define table structures. For example, if we want to save records of Student Data, then we will have to create a table named Student, add columns to it, like student_id, student_name etc, this is called defined schema, where in we define the structure before saving any data.
If in future we plan to add some more related data in our Student table, then we will have to add a new column to our table. Which is easy, if we have less data in our tables, but what if we have millions of records. Migration to the updated schema would be a hectic job. NoSQL databases solve this problem, as in a NoSQL database, schema definition is not required.
- Sharding In Sharding, large databases are partitioned into small, faster and easily manageable databases.
The (classic) Relational Databases follow a vertical architecture where in a single server holds the data, as all the data is related. Relational Databases does not provide Sharding feature by default. NoSQL Databases have the Sharding feature as default. No additional efforts required. They automatically spread the data across servers, fetch the data in the fastest time from the server which is free, while maintaining the integrity of data.
- Replication Auto data replication is also supported in NoSQL databases by default. Hence, if one DB server goes down, data is restored using its copy created on another server in network.
One single main benefit it has over MySQL is its ability to handle large unstructured data. It is magically faster because it allows users to query in a different manner that is more sensitive to workload. Developers note that MySQL is quite slower in comparison to MongoDB when it comes to dealing with large databases.
When designing schemas in Mongo DB, expecially the first times, a quick useful checklist to choose whether or not to use embedded documents in one-to-many relation.
So here is the checklist:
-
Type of query: ask yourself what could be the best model representation for the most frequent queries you'll need to do. Everytime I'll get the parent document I'll always (or really often) need all the child documents. Answer: Nested.
-
Data model lifecycle: think about the life cycle of the container document and its content: make sense that child documents will still have to exist when the parent document is deleted? If the answer is "no" nested is the way.
-
Direct access: how many times you need to easily access the nested document (without caring of its container). If you need this, go for a flat design with references.
-
Number of nested object: a MongoDB document has a size limit of 16MB (quite big amount of data). If your subcollection can growth without limits go flat.