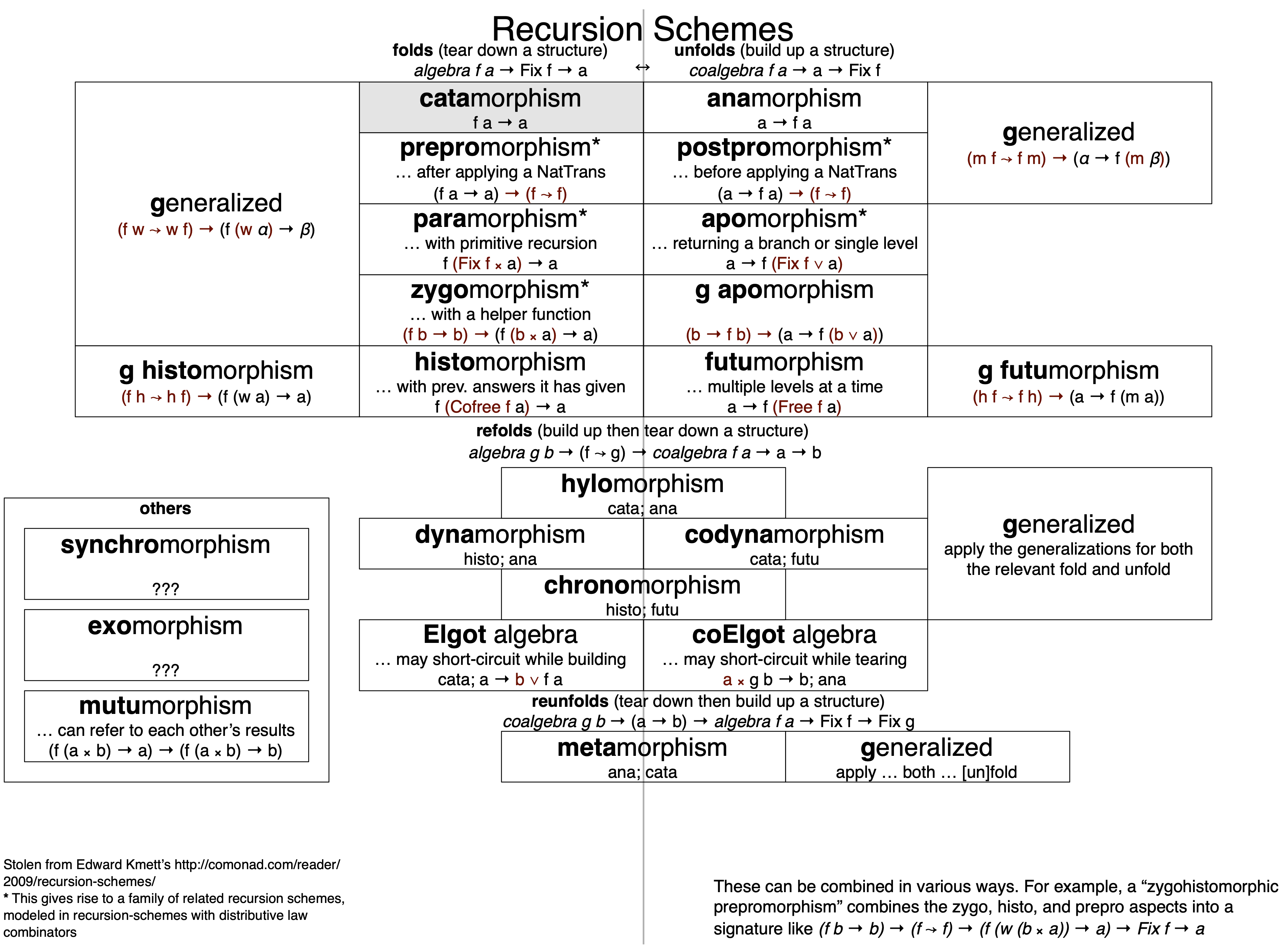
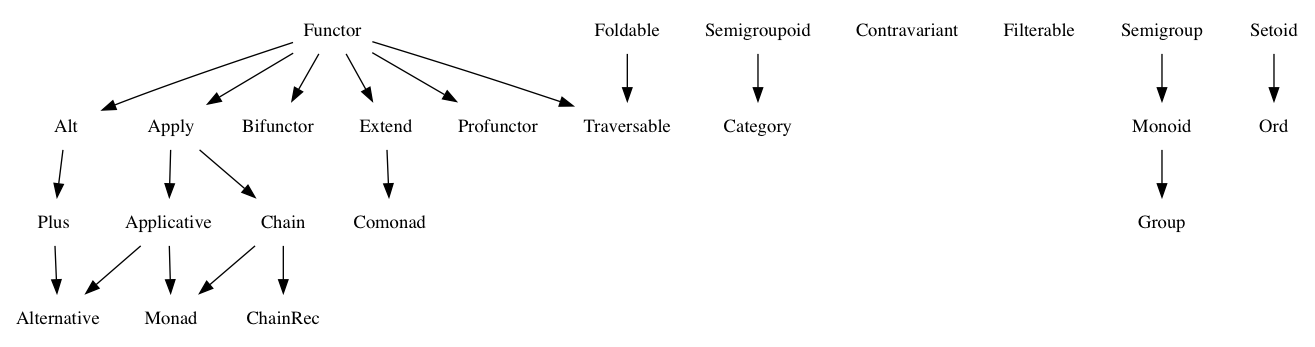
Last active
July 4, 2023 17:16
-
-
Save tkersey/69c36bcf40e23f7ef5c82a9c63983a13 to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
[fit] Group-like
[fit] Ring-like
[fit] Lattice-like
[fit] Module-like
[fit] Algebra-like
[fit] connected by the absorption law
protocol Magma {
static func <> (lhs: Self, rhs: Self) -> Self
}interface Magma<A> {
readonly concat: (x: A, y: A) => A
}protocol Semigroup: Magma {}interface Semigroup<A> extends Magma<A> {}protocol Monoid: Semigroup {
static var empty: Self { get }
}interface Monoid<A> extends Semigroup<A> {
readonly empty: A
}struct Sum<A: Numeric>: Monoid {
let sum: A
init(_ sum: A) {
self.sum = sum
}
static func <> (lhs: Sum, rhs: Sum) -> Sum {
self.init(lhs.sum + rhs.sum)
}
static var empty: Sum {
0
}
}const Sum: monoid<number> = {
empty: 0,
concat: (u: number, v: number) => u + v
}struct Product<A: Numeric>: Monoid {
let product: A
init(_ product: A) {
self.product = product
}
static func <> (lhs: Product, rhs: Product) -> Product {
self.init(lhs.product * rhs.product)
}
static var empty: Product {
1
}
}const Product: monoid<number> = {
empty: 1,
concat: (u: number, v: number) => u * v
}struct Endo<A>: Monoid {
let call: (A) -> A
init(_ call: @escaping (A) -> A) {
self.call = call
}
static func <> (lhs: Endo<A>, rhs: Endo<A>) -> Endo<A> {
.init { rhs.call(lhs.call($0)) }
}
static var empty: Endo<A> {
.init { $0 }
}
}const Endo = <A>(): Monoid<Endo<A>> => ({
empty: (a) => a,
concat: (lhs: Endo<A>, rhs: Endo<A>) => rhs(lhs())
})struct All: Monoid {
let bool: Bool
init(_ bool: Bool) {
self.bool = bool
}
static func <> (lhs: Bool, rhs: Bool) -> Bool {
.init(lhs.bool && rhs.bool)
}
static var empty: Bool {
.init(true)
}
}const All: monoid<boolean> = {
empty: true,
concat: (x, y) => x && y
}struct Any: Monoid {
let bool: Bool
init(_ bool: Bool) {
self.bool = bool
}
static func <> (lhs: Bool, rhs: Bool) -> Bool {
.init(lhs.bool || rhs.bool)
}
static var empty: Bool {
.init(false)
}
}const Any: monoid<boolean> = {
empty: false,
concat: (x, y) => x || y
}extension Array: Monoid {
static func <> (lhs: Array, rhs: Array) -> Array {
lhs + rhs
}
static var empty: Array {
[]
}
}const List: monoid<Array<A>> = {
empty: [],
concat: (x, y) => x.concat(y)
}extension String: Monoid {
static func <> (lhs: String, rhs: String) -> String {
lhs + rhs
}
static var empty: String {
""
}
}const String: monoid<string> = {
empty: '',
concat: (x, y) => x + y
}extension Optional: Monoid where Wrapped: Monoid {
static func <> (lhs: Optioanl, rhs: Optional) -> Optional {
switch (lhs, rhs) {
case (.none, _):
return rhs
case (_, .none):
return lhs
case let (.some(l), some(r)):
return .some(l <> r)
}
}
static var empty: Optional {
.none
}
}export interface None {
readonly _tag: 'None'
}
export interface Some<A> {
readonly _tag: 'Some'
readonly value: A
}
export type Option<A> = None | Some<A>
export const isSome: <A>(fa: Option<A>) => fa is Some<A> = _.isSome
export const isNone = (fa: Option<unknown>): fa is None => fa._tag === 'None'
export const Maybe = <A>(S: Semigroup<A>): Monoid<Option<A>> => ({
empty: none,
concat: (x, y) => (isNone(x) ? y : isNone(y) ? x : some(S.concat(x.value, y.value)))
})reverse :: [a] -> [a]
reverse [] = []
reverse (a : as) = reverse as ++ [a]instance Monoid [a] where
mempty = []
mappend as bs = as ++ bs[fit] Cayley theorem
[fit] Cayley theorem
type DList a = [a] -> [a]rep :: [a] -> DList a
rep as = \xs -> as ++ xsunRep :: DList a -> [a]
unRep f = f []rep [] = id
rep (xs ++ ys) = rep xs . rep ysrev :: [a] -> DList a
rev [] = rep []
rev (a : as) = rev as . rep [a]fastReverse :: [a] -> [a]
fastReverse = unRep . revprotocol Foldable {
associatedtype A
associatedtype B
func foldr(_ folder : (A) -> (B) -> B, _ initial : B) -> B
func foldl(_ folder : (B) -> (A) -> B, _ initial : B) -> B
func foldMap<M : Monoid>(_ map : (A) -> M) -> M
}
https://github.com/alskipp/Monoid/commit/86b6f0f85e85f0eec5a005f092501f8dc8f2da80[fit] How abstract algebra
How the abstract algebra and probabilistic data structures help solve fast versus big data issues that many are struggling with.
autoscale: true
| Symbols | Operations | Laws |
|---|---|---|
| 0, 1, 2, x, y, z | +, –, ×, % | 0 + x = x |
| Symbols | Operations | Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Types | Type constructors | ? |
| (Void, Int, Bool) | (Optional, Either) | ? |
| Symbols | Operations | Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Things | Ways to make new things |
Rules the things follow |
enum Never {}type Void = neverstruct Unit {}type Unit = voidenum Bool {
case true
case false
}type Bool = False | Trueenum Three {
case one
case two
case three
}type Three = One | Two | Threeenum Either<L, R> {
case left(L)
case right(R)
}type Either<L, R> = Left<L> | Right<R>Either<Bool, Three>
.left(.false)
.left(.true)
.right(.one)
.right(.two)
.right(.three)Either<Bool, Three>
Left<False>
Left<True>
Right<One>
Right<Two>
Right<Three>struct Pair<First, Second> {
let first: First
let second: Second
}type Pair<First, Second> = [First, Second]Pair<Bool, Three>
Pair(.false, .one)
Pair(.false, .two)
Pair(.false, .three)
Pair(.true, .one)
Pair(.true, .two)
Pair(.true, .three)Pair<False,One>
Pair<False,Two>
Pair<False,Three>
Pair<True,One>
Pair<True,Two>
Pair<True,Three>struct Reader<R, A> {
let run: (R) -> A
}interface Reader<R, A> {
(r: R): A
}Set<(Three) -> Bool>
(.false, .false, .false),
(.false, .false, .true),
(.false, .true, .true),
(.false, .true, .false),
(.true, .true, .true),
(.true, .true, .false),
(.true, .false, .false),
(.true, .false, .true),struct Optional<A> {
case none
case some(A)
}type Option<A> = None | Some<A>enum List<A> {
case empty
indirect case cons(A, List<A>)
}type List<A> = Nil | Cons<Pair<A, List<A>>>$$List = 1 / (1 - A)$$
List<A> = 1 / (1 - A)
= 1 + A + A×A + A×A×A + A×A×A×A + ...
= 1 + A + A² + A³ + A⁴ + ...
enum Tree<A> {
case empty
indirect case node(A, Pair<Tree<A>, Tree<A>>)
}type Tree<A> = Empty | Node<A, Pair<Tree<A>, Tree<A>>>[fit] Quadratic equation
autoscale: true
[fit] Code Review1
[fit] Sustainable Pace2
Footnotes
-
[Intro to Empirical Software Engineering: What We Know We Don't Know]((https://youtu.be/WELBnE33dpY?t=1698) ↩
-
Intro to Empirical Software Engineering: What We Know We Don't Know ↩
autoscale: true
| Syntax | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| x | Variable | A character or string representing a parameter or mathematical/logical value |
| (λx.M) | Abstraction | Function definition (M is a lambda term). The variable x becomes bound in the expression |
| (M N) | Application | Applying a function to an argument. M and N are lambda terms |
the idea that the reader can make sense of the code directly in front of them, without going on a journey discovering how the code works.
| Logic | Types | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| propositions | types | objects |
| proofs | terms | arrows |
| proof of proposition A | inhabitation of type A | arrow f: t → A |
| implication | function type | exponential |
| conjunction | product type | product |
| disjunction | sum type | coproduct |
| falsity | void type (empty) | initial object |
| truth | unit type (singleton) | terminal object T |
| Logic | Types | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| propositions | types | objects |
| proofs | terms | arrows |
| proof of proposition A | inhabitation of type A | arrow f: t → A |
| implication | function type | exponential |
| conjunction | product type | product |
| disjunction | sum type | coproduct |
| falsity | void type (empty) | initial object |
| truth | unit type (singleton) | terminal object T |
type Dollars = number & { readonly __tag: unique symbol };Just another name for a regular function to make it clear that it is defined for all elements of its input.
head :: [a] -> asafehead :: [a] -> Maybe atype NonEmptyArray<T> = [T, ...T[]];[fit] Parse don't validate
interface Writer<W, A> {
(): [A, W]
}UI = fn(state)[fit] Janus
[fit] Curry-Howard
^ A direct relationship between computer programs and mathematical proofs ^ Pictures and bios of Curry and Howard ^ Give a little explaination of your passion for mathematical thinking
| Logic | Types |
|---|---|
| propositions | types |
| proofs | terms |
| proof of proposition A | inhabitation of type A |
| implication | function type |
| conjunction | product type |
| disjunction | sum type |
| falsity | void type (empty) |
| truth | unit type (singleton) |
| Logic | Types |
|---|---|
| propositions | types |
| proofs | terms |
| proof of proposition A | inhabitation of type A |
| implication | function type |
| conjunction | product type |
| disjunction | sum type |
| falsity | void type (empty) |
| truth | unit type (singleton) |
| ^ It's enough to have an instance (inhabitant) of a type to prove it |
| Logic | Types |
|---|---|
| propositions | types |
| proofs | terms |
| proof of proposition A | inhabitation of type A |
| implication | function type |
| conjunction | product type |
| disjunction | sum type |
| falsity | void type (empty) |
| truth | unit type (singleton) |
[fit] Parse, don't validate
const head = (i: Array<a>): a = {...}const head = (i: Array<a>): Maybe<a> = {...}export interface None {
readonly _tag: 'None'
}
export interface Some<A> {
readonly _tag: 'Some'
readonly value: A
}
export type Maybe<A> = None | Some<A>| Logic | Types | Categories |
|---|---|---|
| propositions | types | objects |
| proofs | terms | arrows |
| proof of proposition A | inhabitation of type A | arrow f: t → A |
| implication | function type | exponential |
| conjunction | product type | product |
| disjunction | sum type | coproduct |
| falsity | void type (empty) | initial object |
| truth | unit type (singleton) | terminal object T |
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment