Standard escape codes are prefixed with Escape:
- Ctrl-Key:
^[ - Octal:
\033 - Unicode:
\u001b - Hexadecimal:
\x1B - Decimal:
27
Followed by the command, somtimes delimited by opening square bracket ([), known as a Control Sequence Introducer (CSI), optionally followed by arguments and the command itself.
Arguments are delimeted by semi colon (;).
For example:
\x1b[1;31m # Set style to bold, red foreground.ESC- sequence starting withESC(\x1B)CSI- Control Sequence Introducer: sequence starting withESC [or CSI (\x9B)DCS- Device Control String: sequence starting withESC Por DCS (\x90)OSC- Operating System Command: sequence starting withESC ]or OSC (\x9D)
Any whitespaces between sequences and arguments should be ignored. They are present for improved readability.
| Name | decimal | octal | hex | C-escape | Ctrl-Key | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BEL |
7 | 007 | 0x07 | \a |
^G |
Terminal bell |
BS |
8 | 010 | 0x08 | \b |
^H |
Backspace |
HT |
9 | 011 | 0x09 | \t |
^I |
Horizontal TAB |
LF |
10 | 012 | 0x0A | \n |
^J |
Linefeed (newline) |
VT |
11 | 013 | 0x0B | \v |
^K |
Vertical TAB |
FF |
12 | 014 | 0x0C | \f |
^L |
Formfeed (also: New page NP) |
CR |
13 | 015 | 0x0D | \r |
^M |
Carriage return |
ESC |
27 | 033 | 0x1B | \e* |
^[ |
Escape character |
DEL |
127 | 177 | 0x7F | <none> |
<none> |
Delete character |
Note: Some control escape sequences, like
\eforESC, are not guaranteed to work in all languages and compilers. It is recommended to use the decimal, octal or hex representation as escape code.
Note: The Ctrl-Key representation is simply associating the non-printable characters from ASCII code 1 with the printable (letter) characters from ASCII code 65 ("A"). ASCII code 1 would be
^A(Ctrl-A), while ASCII code 7 (BEL) would be^G(Ctrl-G). This is a common representation (and input method) and historically comes from one of the VT series of terminals.
| ESC Code Sequence | Description |
|---|---|
ESC[H |
moves cursor to home position (0, 0) |
ESC[{line};{column}H ESC[{line};{column}f |
moves cursor to line #, column # |
ESC[#A |
moves cursor up # lines |
ESC[#B |
moves cursor down # lines |
ESC[#C |
moves cursor right # columns |
ESC[#D |
moves cursor left # columns |
ESC[#E |
moves cursor to beginning of next line, # lines down |
ESC[#F |
moves cursor to beginning of previous line, # lines up |
ESC[#G |
moves cursor to column # |
ESC[6n |
request cursor position (reports as ESC[#;#R) |
ESC M |
moves cursor one line up, scrolling if needed |
ESC 7 |
save cursor position (DEC) |
ESC 8 |
restores the cursor to the last saved position (DEC) |
ESC[s |
save cursor position (SCO) |
ESC[u |
restores the cursor to the last saved position (SCO) |
Note: Some sequences, like saving and restoring cursors, are private sequences and are not standardized. While some terminal emulators (i.e. xterm and derived) support both SCO and DEC sequences, they are likely to have different functionality. It is therefore recommended to use DEC sequences.
| ESC Code Sequence | Description |
|---|---|
ESC[J |
erase in display (same as ESC[0J) |
ESC[0J |
erase from cursor until end of screen |
ESC[1J |
erase from cursor to beginning of screen |
ESC[2J |
erase entire screen |
ESC[3J |
erase saved lines |
ESC[K |
erase in line (same as ESC[0K) |
ESC[0K |
erase from cursor to end of line |
ESC[1K |
erase start of line to the cursor |
ESC[2K |
erase the entire line |
Note: Erasing the line won't move the cursor, meaning that the cursor will stay at the last position it was at before the line was erased. You can use
\rafter erasing the line, to return the cursor to the start of the current line.
| ESC Code Sequence | Reset Sequence | Description |
|---|---|---|
ESC[1;34;{...}m |
Set graphics modes for cell, separated by semicolon (;). |
|
ESC[0m |
reset all modes (styles and colors) | |
ESC[1m |
ESC[22m |
set bold mode. |
ESC[2m |
ESC[22m |
set dim/faint mode. |
ESC[3m |
ESC[23m |
set italic mode. |
ESC[4m |
ESC[24m |
set underline mode. |
ESC[5m |
ESC[25m |
set blinking mode |
ESC[7m |
ESC[27m |
set inverse/reverse mode |
ESC[8m |
ESC[28m |
set hidden/invisible mode |
ESC[9m |
ESC[29m |
set strikethrough mode. |
Note: Some terminals may not support some of the graphic mode sequences listed above.
Note: Both dim and bold modes are reset with the
ESC[22msequence. TheESC[21msequence is a non-specified sequence for double underline mode and only work in some terminals and is reset withESC[24m.
Most terminals support 8 and 16 colors, as well as 256 (8-bit) colors. These colors are set by the user, but have commonly defined meanings.
| Color Name | Foreground Color Code | Background Color Code |
|---|---|---|
| Black | 30 |
40 |
| Red | 31 |
41 |
| Green | 32 |
42 |
| Yellow | 33 |
43 |
| Blue | 34 |
44 |
| Magenta | 35 |
45 |
| Cyan | 36 |
46 |
| White | 37 |
47 |
| Default | 39 |
49 |
| Reset | 0 |
0 |
Note: the Reset color is the reset code that resets all colors and text effects, Use Default color to reset colors only.
Most terminals, apart from the basic set of 8 colors, also support the "bright" or "bold" colors. These have their own set of codes, mirroring the normal colors, but with an additional ;1 in their codes:
# Set style to bold, red foreground.
\x1b[1;31mHello
# Set style to dimmed white foreground with red background.
\x1b[2;37;41mWorldTerminals that support the aixterm specification provides bright versions of the ISO colors, without the need to use the bold modifier:
| Color Name | Foreground Color Code | Background Color Code |
|---|---|---|
| Bright Black | 90 |
100 |
| Bright Red | 91 |
101 |
| Bright Green | 92 |
102 |
| Bright Yellow | 93 |
103 |
| Bright Blue | 94 |
104 |
| Bright Magenta | 95 |
105 |
| Bright Cyan | 96 |
106 |
| Bright White | 97 |
107 |
The following escape codes tells the terminal to use the given color ID:
| ESC Code Sequence | Description |
|---|---|
ESC[38;5;{ID}m |
Set foreground color. |
ESC[48;5;{ID}m |
Set background color. |
Where {ID} should be replaced with the color index from 0 to 255 of the following color table:
The table starts with the original 16 colors (0-15).
The proceeding 216 colors (16-231) or formed by a 3bpc RGB value offset by 16, packed into a single value.
The final 24 colors (232-255) are grayscale starting from a shade slighly lighter than black, ranging up to shade slightly darker than white.
Some emulators interpret these steps as linear increments (256 / 24) on all three channels, although some emulators may explicitly define these values.
More modern terminals supports Truecolor (24-bit RGB), which allows you to set foreground and background colors using RGB.
These escape sequences are usually not well documented.
| ESC Code Sequence | Description |
|---|---|
ESC[38;2;{r};{g};{b}m |
Set foreground color as RGB. |
ESC[48;2;{r};{g};{b}m |
Set background color as RGB. |
Note that
;38and;48corresponds to the 16 color sequence and is interpreted by the terminal to set the foreground and background color respectively. Where as;2and;5sets the color format.
| ESC Code Sequence | Description |
|---|---|
ESC[={value}h |
Changes the screen width or type to the mode specified by value. |
ESC[=0h |
40 x 25 monochrome (text) |
ESC[=1h |
40 x 25 color (text) |
ESC[=2h |
80 x 25 monochrome (text) |
ESC[=3h |
80 x 25 color (text) |
ESC[=4h |
320 x 200 4-color (graphics) |
ESC[=5h |
320 x 200 monochrome (graphics) |
ESC[=6h |
640 x 200 monochrome (graphics) |
ESC[=7h |
Enables line wrapping |
ESC[=13h |
320 x 200 color (graphics) |
ESC[=14h |
640 x 200 color (16-color graphics) |
ESC[=15h |
640 x 350 monochrome (2-color graphics) |
ESC[=16h |
640 x 350 color (16-color graphics) |
ESC[=17h |
640 x 480 monochrome (2-color graphics) |
ESC[=18h |
640 x 480 color (16-color graphics) |
ESC[=19h |
320 x 200 color (256-color graphics) |
ESC[={value}l |
Resets the mode by using the same values that Set Mode uses, except for 7, which disables line wrapping. The last character in this escape sequence is a lowercase L. |
These are some examples of private modes, which are not defined by the specification, but are implemented in most terminals.
| ESC Code Sequence | Description |
|---|---|
ESC[?25l |
make cursor invisible |
ESC[?25h |
make cursor visible |
ESC[?47l |
restore screen |
ESC[?47h |
save screen |
ESC[?1049h |
enables the alternative buffer |
ESC[?1049l |
disables the alternative buffer |
Refer to the XTerm Control Sequences for a more in-depth list of private modes defined by XTerm.
Note: While these modes may be supported by the most terminals, some may not work in multiplexers like tmux.
ESC[{code};{string};{...}pRedefines a keyboard key to a specified string.
The parameters for this escape sequence are defined as follows:
-
codeis one or more of the values listed in the following table. These values represent keyboard keys and key combinations. When using these values in a command, you must type the semicolons shown in this table in addition to the semicolons required by the escape sequence. The codes in parentheses are not available on some keyboards.ANSI.SYSwill not interpret the codes in parentheses for those keyboards unless you specify the/Xswitch in theDEVICEcommand forANSI.SYS. -
stringis either the ASCII code for a single character or a string contained in quotation marks. For example, both 65 and "A" can be used to represent an uppercase A.
IMPORTANT: Some of the values in the following table are not valid for all computers. Check your computer's documentation for values that are different.
| Key | Code | SHIFT+code | CTRL+code | ALT+code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0;59 | 0;84 | 0;94 | 0;104 |
| F2 | 0;60 | 0;85 | 0;95 | 0;105 |
| F3 | 0;61 | 0;86 | 0;96 | 0;106 |
| F4 | 0;62 | 0;87 | 0;97 | 0;107 |
| F5 | 0;63 | 0;88 | 0;98 | 0;108 |
| F6 | 0;64 | 0;89 | 0;99 | 0;109 |
| F7 | 0;65 | 0;90 | 0;100 | 0;110 |
| F8 | 0;66 | 0;91 | 0;101 | 0;111 |
| F9 | 0;67 | 0;92 | 0;102 | 0;112 |
| F10 | 0;68 | 0;93 | 0;103 | 0;113 |
| F11 | 0;133 | 0;135 | 0;137 | 0;139 |
| F12 | 0;134 | 0;136 | 0;138 | 0;140 |
| HOME (num keypad) | 0;71 | 55 | 0;119 | -- |
| UP ARROW (num keypad) | 0;72 | 56 | (0;141) | -- |
| PAGE UP (num keypad) | 0;73 | 57 | 0;132 | -- |
| LEFT ARROW (num keypad) | 0;75 | 52 | 0;115 | -- |
| RIGHT ARROW (num keypad) | 0;77 | 54 | 0;116 | -- |
| END (num keypad) | 0;79 | 49 | 0;117 | -- |
| DOWN ARROW (num keypad) | 0;80 | 50 | (0;145) | -- |
| PAGE DOWN (num keypad) | 0;81 | 51 | 0;118 | -- |
| INSERT (num keypad) | 0;82 | 48 | (0;146) | -- |
| DELETE (num keypad) | 0;83 | 46 | (0;147) | -- |
| HOME | (224;71) | (224;71) | (224;119) | (224;151) |
| UP ARROW | (224;72) | (224;72) | (224;141) | (224;152) |
| PAGE UP | (224;73) | (224;73) | (224;132) | (224;153) |
| LEFT ARROW | (224;75) | (224;75) | (224;115) | (224;155) |
| RIGHT ARROW | (224;77) | (224;77) | (224;116) | (224;157) |
| END | (224;79) | (224;79) | (224;117) | (224;159) |
| DOWN ARROW | (224;80) | (224;80) | (224;145) | (224;154) |
| PAGE DOWN | (224;81) | (224;81) | (224;118) | (224;161) |
| INSERT | (224;82) | (224;82) | (224;146) | (224;162) |
| DELETE | (224;83) | (224;83) | (224;147) | (224;163) |
| PRINT SCREEN | -- | -- | 0;114 | -- |
| PAUSE/BREAK | -- | -- | 0;0 | -- |
| BACKSPACE | 8 | 8 | 127 | (0) |
| ENTER | 13 | -- | 10 | (0 |
| TAB | 9 | 0;15 | (0;148) | (0;165) |
| NULL | 0;3 | -- | -- | -- |
| A | 97 | 65 | 1 | 0;30 |
| B | 98 | 66 | 2 | 0;48 |
| C | 99 | 66 | 3 | 0;46 |
| D | 100 | 68 | 4 | 0;32 |
| E | 101 | 69 | 5 | 0;18 |
| F | 102 | 70 | 6 | 0;33 |
| G | 103 | 71 | 7 | 0;34 |
| H | 104 | 72 | 8 | 0;35 |
| I | 105 | 73 | 9 | 0;23 |
| J | 106 | 74 | 10 | 0;36 |
| K | 107 | 75 | 11 | 0;37 |
| L | 108 | 76 | 12 | 0;38 |
| M | 109 | 77 | 13 | 0;50 |
| N | 110 | 78 | 14 | 0;49 |
| O | 111 | 79 | 15 | 0;24 |
| P | 112 | 80 | 16 | 0;25 |
| Q | 113 | 81 | 17 | 0;16 |
| R | 114 | 82 | 18 | 0;19 |
| S | 115 | 83 | 19 | 0;31 |
| T | 116 | 84 | 20 | 0;20 |
| U | 117 | 85 | 21 | 0;22 |
| V | 118 | 86 | 22 | 0;47 |
| W | 119 | 87 | 23 | 0;17 |
| X | 120 | 88 | 24 | 0;45 |
| Y | 121 | 89 | 25 | 0;21 |
| Z | 122 | 90 | 26 | 0;44 |
| 1 | 49 | 33 | -- | 0;120 |
| 2 | 50 | 64 | 0 | 0;121 |
| 3 | 51 | 35 | -- | 0;122 |
| 4 | 52 | 36 | -- | 0;123 |
| 5 | 53 | 37 | -- | 0;124 |
| 6 | 54 | 94 | 30 | 0;125 |
| 7 | 55 | 38 | -- | 0;126 |
| 8 | 56 | 42 | -- | 0;126 |
| 9 | 57 | 40 | -- | 0;127 |
| 0 | 48 | 41 | -- | 0;129 |
| - | 45 | 95 | 31 | 0;130 |
| = | 61 | 43 | --- | 0;131 |
| [ | 91 | 123 | 27 | 0;26 |
| ] | 93 | 125 | 29 | 0;27 |
| 92 | 124 | 28 | 0;43 | |
| ; | 59 | 58 | -- | 0;39 |
| ' | 39 | 34 | -- | 0;40 |
| , | 44 | 60 | -- | 0;51 |
| . | 46 | 62 | -- | 0;52 |
| / | 47 | 63 | -- | 0;53 |
| ` | 96 | 126 | -- | (0;41) |
| ENTER (keypad) | 13 | -- | 10 | (0;166) |
| / (keypad) | 47 | 47 | (0;142) | (0;74) |
| * (keypad) | 42 | (0;144) | (0;78) | -- |
| - (keypad) | 45 | 45 | (0;149) | (0;164) |
| + (keypad) | 43 | 43 | (0;150) | (0;55) |
| 5 (keypad) | (0;76) | 53 | (0;143) | -- |
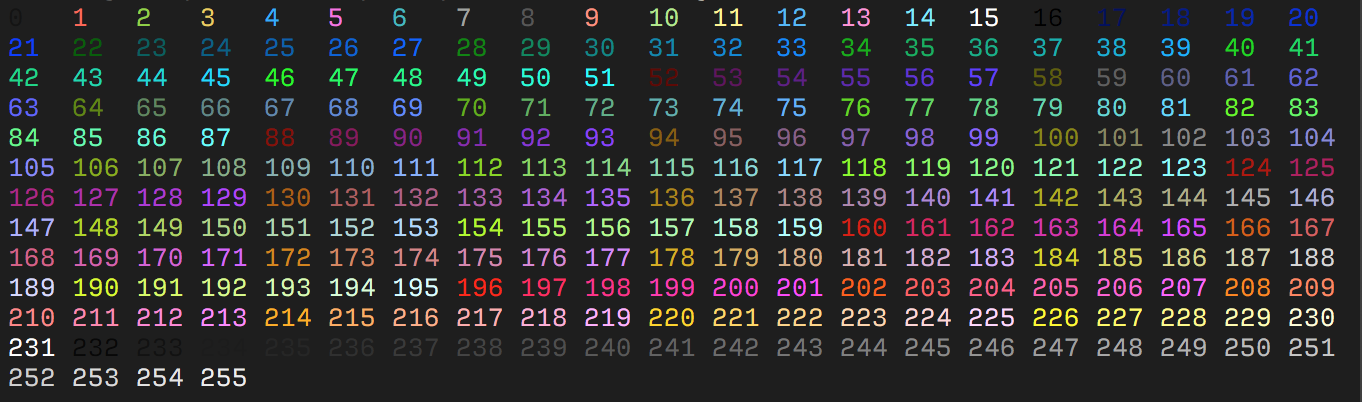
@BDisp It definitely should be "the middle 216."
256 (all) - 16 (first) - 24 (last) = 216 (middle). Each RGB component has 6 levels, including zero, 6^3 = 216.
Also, the title should say "256-colour" not "255-colour."