Create a template service file at /etc/systemd/system/secure-tunnel@.service. The template parameter will correspond to the name
of target host:
[Unit]
Description=Setup a secure tunnel to %I
After=network.target
[Service]
Environment="LOCAL_ADDR=localhost"
EnvironmentFile=/etc/default/secure-tunnel@%i
ExecStart=/usr/bin/ssh -NT -o ServerAliveInterval=60 -o ExitOnForwardFailure=yes -L ${LOCAL_ADDR}:${LOCAL_PORT}:localhost:${REMOTE_PORT} ${TARGET}
# Restart every >2 seconds to avoid StartLimitInterval failure
RestartSec=5
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetWe need a configuration file (inside /etc/default) for each target host we will be creating tunnels for. For example, let's assume we want to tunnel to a host named jupiter (probably aliased in /etc/hosts). Create the file at /etc/default/secure-tunnel@jupiter:
TARGET=jupiter
LOCAL_ADDR=0.0.0.0
LOCAL_PORT=20022
REMOTE_PORT=22
Note that for the above to work we need to have allready setup a password-less SSH login to target (e.g. by giving access to a non-protected private key).
Now we can start the service instance:
systemctl start secure-tunnel@jupiter.service
systemctl status secure-tunnel@jupiter.service
Or enable it, so it get's started at boot time:
systemctl enable secure-tunnel@jupiter.service

Hello,
i have at least the same example
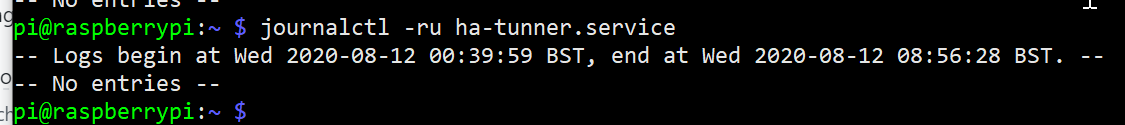
But it do not start. i get

It also do not shows any logs with command

PLease advice me what have i've done wrong?
Thanks a lot!